13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2012; 2(9):880-888. doi:10.7150/thno.3899 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species in Sonodynamically Induced Apoptosis Using a Novel Porphyrin Derivative
1. School of Pharmacy, Yokohama College of Pharmacy, 601, Matano-cho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 245-0066, Japan;
2. Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering, Tohoku University, Aoba 6-6-05, Aramaki, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980-8579, Japan;
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University, 2-2-1 Miyama, Funabashi, Chiba 274-8510, Japan.
Abstract
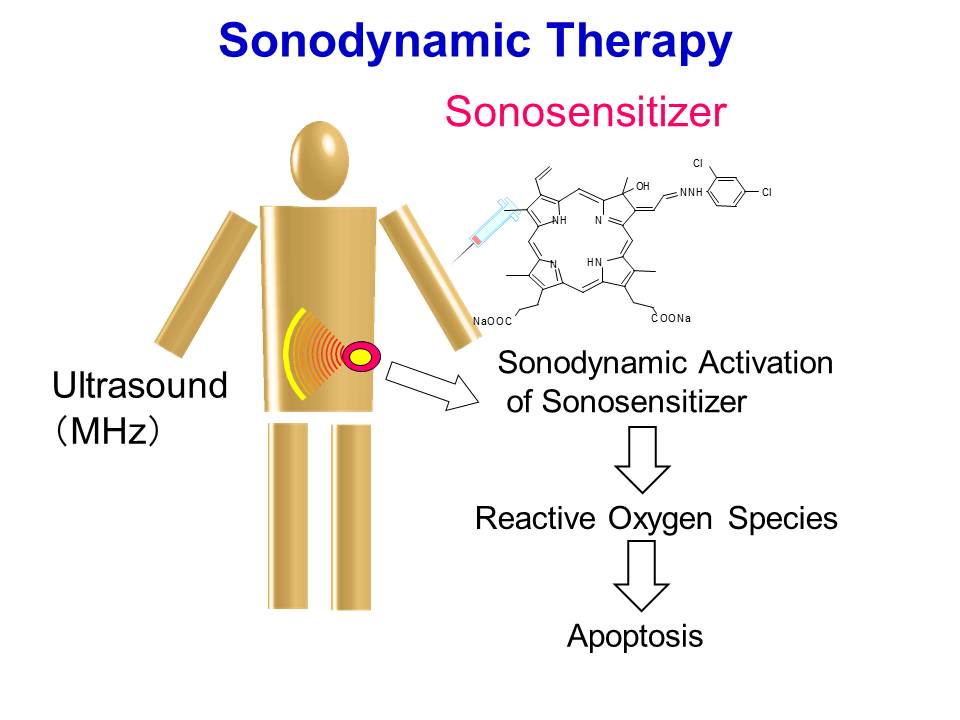
In this study, we investigated the induction of apoptosis by ultrasound in the presence of the novel porphyrin derivative DCPH-P-Na(I). HL-60 cells were exposed to ultrasound for up to 3 min in the presence and absence of DCPH-P-Na(I), and the induction of apoptosis was examined by analyzing cell morphology, DNA fragmentation, and caspase-3 activity. Reactive oxygen species were measured by means of ESR and spin trapping technique. Cells treated with 8 μM DCPH-P-Na(I) and ultrasound clearly showed membrane blebbing and cell shrinkage, whereas significant morphologic changes were not observed in cells exposed to either ultrasound or DCPH-P-Na(I) alone. Also, DNA ladder formation and caspase-3 activation were observed in cells treated with both ultrasound and DCPH-P-Na(I) but not in cells treated with ultrasound or DCPH-P-Na(I) alone. In addition, the combination of DCPH-P-Na(I) and the same acoustical arrangement of ultrasound substantially enhanced nitroxide generation by the cells. Sonodynamically induced apoptosis, caspase-3 activation, and nitroxide generation were significantly suppressed by histidine. These results indicate that the combination of ultrasound and DCPH-P-Na(I) induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. The significant reduction in sonodynamically induced apoptosis, nitroxide generation, and caspase-3 activation by histidine suggests active species such as singlet oxygen are important in the sonodynamic induction of apoptosis. These experimental results support the possibility of sonodynamic treatment for cancer using the induction of apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Sonodynamic therapy, Ultrasound, DCPH-P-Na(I), HL-60 cells, Reactive Oxygen, Caspase-3.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact