13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2014; 4(10):1014-1025. doi:10.7150/thno.9575 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging for the Detection of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening
1. Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences, National Tsing Hua University, No. 101, Section 2, Kuang-Fu Road, Hsinchu, Taiwan 30013;
2. Department of Electrical Engineering, Chang-Gung University, 259 Wen-Hwa 1st Road, Kuei-Shan, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan 33302;
3. Department of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Center, Chang Gung University and Memorial Hospital, No. 5, Fu-Shing Road, Kuei-Shan, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan 33305.
Abstract
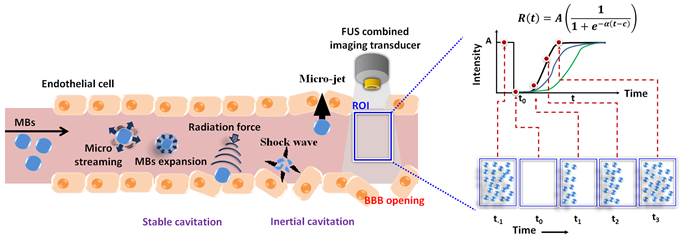
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) can be transiently and locally opened by focused ultrasound (FUS) in the presence of microbubbles (MBs). Various imaging modalities and contrast agents have been used to monitor this process. Unfortunately, direct ultrasound imaging of BBB opening with MBs as contrast agent is not feasible, due to the inability of MBs to penetrate brain parenchyma. However, FUS-induced BBB opening is accompanied by changes in blood flow and perfusion, suggesting the possibility of perfusion-based ultrasound imaging. Here we evaluated the use of MB destruction-replenishment, which was originally developed for analysis of ultrasound perfusion kinetics, for verifying and quantifying FUS-induced BBB opening. MBs were intravenously injected and the BBB was disrupted by 2 MHz FUS with burst-tone exposure at 0.5-0.7 MPa. A perfusion kinetic map was estimated by MB destruction-replenishment time-intensity curve analysis. Our results showed that the scale and distribution of FUS-induced BBB opening could be determined at high resolution by ultrasound perfusion kinetic analysis. The accuracy and sensitivity of this approach was validated by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Our successful demonstration of ultrasound imaging to monitor FUS-induced BBB opening provides a new approach to assess FUS-dependent brain drug delivery, with the benefit of high temporal resolution and convenient integration with the FUS device.
Keywords: focused ultrasound, blood-brain barrier, microbubbles, destruction- replenishment, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact