13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(5):477-488. doi:10.7150/thno.10823 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MRI Visible Drug Eluting Magnetic Microspheres for Transcatheter Intra-Arterial Delivery to Liver Tumors
1. Department of Radiology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA; Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chicago, IL 60611, USA.
2. Department of Radiology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA.
3. Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA.
4. Department of Bioengineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA; Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Evanston, IL, USA; International Institute of Nanotechnology (IIN), Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA; Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chicago, IL 60611, USA. Department of Radiology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA.
Abstract
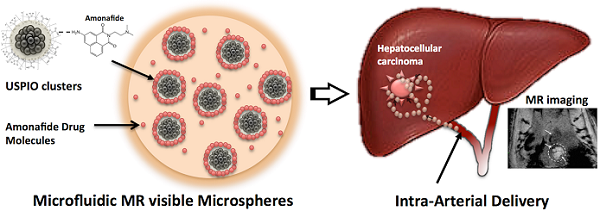
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-visible amonafide-eluting alginate microspheres were developed for targeted arterial-infusion chemotherapy. These alginate microspheres were synthesized using a highly efficient microfluidic gelation process. The microspheres included magnetic clusters formed by USPIO nanoparticles to permit MRI and a sustained drug-release profile. The biocompatibility, MR imaging properties and amonafide release kinetics of these microspheres were investigated during in vitro studies. A xenograft rodent model was used to demonstrate the feasibility to deliver these microspheres to liver tumors using hepatic transcatheter intra-arterial infusions and potential to visualize the intra-hepatic delivery of these microspheres to both liver tumor and normal tissues with MRI immediately after infusion. This approach offer the potential for catheter-directed drug delivery to liver tumors for reduced systemic toxicity and superior therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: MRI, microspheres, liver tumors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact