13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(10):1528-1541. doi:10.7150/thno.15246 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Pharmacokinetic Behaviors of Intravenously Administered siRNA in Glandular Tissues
1. Institute of Molecular Medicine, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China;
2. Suzhou Ribo Life Science Co. Ltd., Jiangsu 215300, China;
3. Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin 300072, China;
4. National Chengdu Center for Safety Evaluation of Drugs, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, Collaborative Innovation Center for Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
Abstract
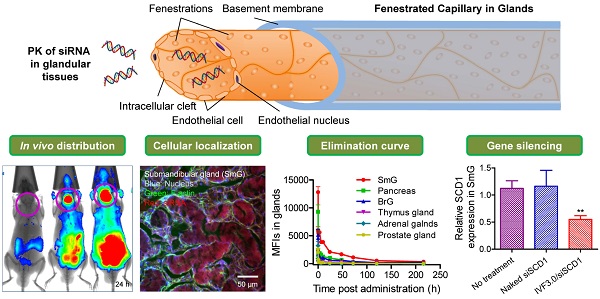
The pharmacokinetics of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) is a pivotal issue for siRNA-based drug development. In this study, we comprehensively investigated the behavior of siRNAs in vivo in various tissues and demonstrated that intravenously-injected naked siRNA accumulated remarkably in the submandibular gland, bulbourethral gland, and pancreas, with a respective half-life of ~22.7, ~45.6, and ~30.3 h. This was further confirmed by gel separation of tissue homogenates and/or supernatants. In vivo imaging and cryosectioning suggested that delivery carriers significantly influence the distribution and elimination profiles of siRNA. Gene-silencing assays revealed that neither naked nor liposome-formulated siRNA resulted in gene knockdown in the submandibular and bulbourethral glands after systemic administration, suggesting that these glands function as drug reservoirs that enable slow siRNA release into the circulation. But robust gene-silencing was achieved by local injection of liposome-encapsulated siRNA into the submandibular gland. Our results enhance understanding of the pharmacokinetic properties of siRNAs and we believe that they will facilitate the development of siRNA therapy, especially for the submandibular gland.
Keywords: siRNA, pharmacokinetics, submandibular gland, biodistribution.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact