13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(3):513-522. doi:10.7150/thno.17596 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Precise Spatially Selective Photothermolysis Using Modulated Femtosecond Lasers and Real-time Multimodal Microscopy Monitoring
1. Imaging Unit - Integrative Oncology Department, BC Cancer Agency Research Center, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
2. Photomedicine Institute - Department of Dermatology and Skin Science, University of British Columbia and Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Abstract
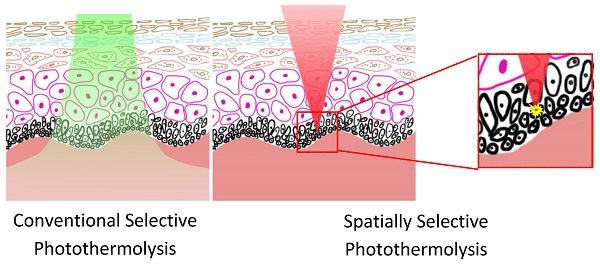
The successful application of lasers in the treatment of skin diseases and cosmetic surgery is largely based on the principle of conventional selective photothermolysis which relies strongly on the difference in the absorption between the therapeutic target and its surroundings. However, when the differentiation in absorption is not sufficient, collateral damage would occur due to indiscriminate and nonspecific tissue heating. To deal with such cases, we introduce a novel spatially selective photothermolysis method based on multiphoton absorption in which the radiant energy of a tightly focused near-infrared femtosecond laser beam can be directed spatially by aiming the laser focal point to the target of interest. We construct a multimodal optical microscope to perform and monitor the spatially selective photothermolysis. We demonstrate that precise alteration of the targeted tissue is achieved while leaving surrounding tissue intact by choosing appropriate femtosecond laser exposure with multimodal optical microscopy monitoring in real time.
Keywords: spatially selective photothermolysis, multiphoton absorption photothermolysis, reflectance confocal microscopy, two-photon fluorescence, second harmonic generation, modulated femtosecond laser.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact