13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(11):2940-2955. doi:10.7150/thno.18845 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Placental Homing Peptide-microRNA Inhibitor Conjugates for Targeted Enhancement of Intrinsic Placental Growth Signaling
1. Maternal and Fetal Health Research Centre, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, UK;
2. Maternal and Fetal Health Research Centre, St. Mary's Hospital, Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester M13 9WL, UK;
3. Present address: Institute of Developmental Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO16 6YD, UK;
4. Present address: Department of Biology, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Edge Hill University, Ormskirk, L39 4QP, UK;
5. Present address: Leeds Institute of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT, UK;
6. Division of Pharmacy and Optometry, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL, UK.
Abstract
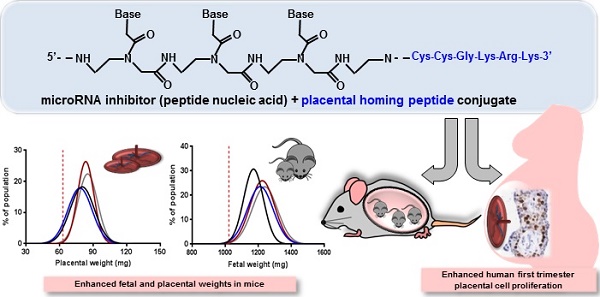
Suboptimal placental growth and development are the underlying cause of many pregnancy complications. No treatments are available, primarily due to the risk of causing fetal teratogenicity. microRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNA sequences that regulate multiple downstream genes; miR-145 and miR675 have previously been identified as negative regulators of placental growth. In this proof of principle study, we explored the feasibility of delivering miRNA inhibitors to the placentas of pregnant mice and developed novel placental homing peptide-microRNA inhibitor conjugates for targeted enhancement of intrinsic placental growth signalling. Scrambled-, miR-145- or miR-675 inhibitor sequences were synthesised from peptide nucleic acids and conjugated to the placental homing peptide CCGKRK. Intravenous administration of the miR-145- and miR-675 conjugates to pregnant C57BL/6J mice significantly increased fetal and placental weights compared to controls; the miR-675 conjugate significantly reduced placental miR-675 expression. When applied to human first trimester placental explants, the miR-145 conjugate significantly reduced placental miR-145 expression, and both conjugates induced significant enhancement of cytotrophoblast proliferation; no effect was observed in term placental explants. This study demonstrates that homing peptide-miRNA inhibitor conjugates can be exploited to promote placental growth; these novel therapeutics may represent an innovative strategy for targeted treatment of compromised placental development.
Keywords: fetal growth restriction, IGF-II, microRNA, placenta, proliferation, pregnancy.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact