13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(15):3759-3767. doi:10.7150/thno.20734 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dual Functioned Pegylated Phospholipid Micelles Containing Cationic Antimicrobial Decapeptide for Treating Sepsis
College of Pharmacy, CMRI, Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, BK21 Plus KNU Multi-Omics Based Creative Drug Research Team, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Republic of Korea
* First two authors contributed equally to this work.
# Current address; College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, 84 Heukseok-ro, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 06974, Republic of Korea
Abstract
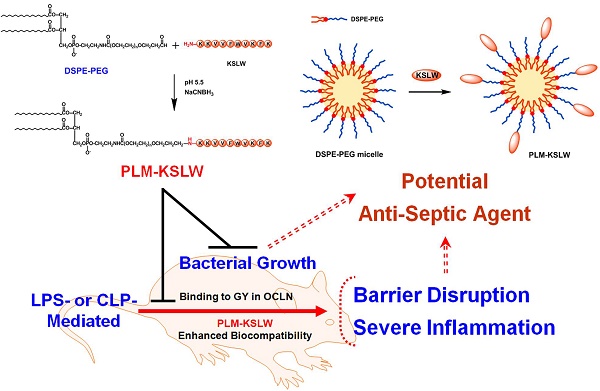
Despite intensive investigation of molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of sepsis, many aspects of sepsis remain unresolved; this hampers the development of appropriate therapeutics. In the present study, we developed a biologic nanomedicine containing a cationic antimicrobial decapeptide KSLW (KKVVFWVKFK), self-associated with biocompatible and biodegradable PEGylated phospholipid micelles (PLM), and analyzed its efficacy for treating sepsis. KSLW was modified with polyethylene glycol (PEG)-aldehyde or was conjugated with distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE) -PEG-aldehyde. We compared the antibacterial and antiseptic effects of PEG-KSLW and PLM-KSLW with those of unmodified KSLW both in vitro and in vivo. We found that the PLM-KSLW improved the survival rate of sepsis mouse models without undesired immune responses, and inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced severe vascular inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells compared with unmodified KSLW or PEG-KSLW. Furthermore, PLM-KSLW dramatically reduced the bacterial count and inhibited bacterial growth. We also found a new role of PLM-KSLW in tightening vascular barrier integrity by binding to the glycine/tyrosine-rich domain of occludin (OCLN). Our results showed that PLM-KSLW had a more effective antiseptic effect than KSLW or PEG-KSLW, possibly because of its high affinity toward OCLN. Moreover, PLM-KSLW could be potentially used to treat severe vascular inflammatory diseases, including sepsis and septic shock.
Keywords: sepsis, KSLW, PEGylation, DSPE, occluding.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact