13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(2):369-383. doi:10.7150/thno.21397 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dual Targeting of Acute Leukemia and Supporting Niche by CXCR4-Directed Theranostics
1. Internal Medicine III, Hematology and Medical Oncology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany;
2. German Cancer Consortium (DKTK) and German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany;
3. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany;
4. Institute of Pharmaceutical Radiochemistry, Technische Universität München, Garching, Germany;
5. Institute of Pathology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany;
6. Research Unit Gene Vectors, Helmholtz Center Munich, Germany;
7. Institute for Pathology, University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany;
8. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany;
9. Department of Internal Medicine II, Hematology and Medical Oncology, University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany.
# These authors contributed equally.
* These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
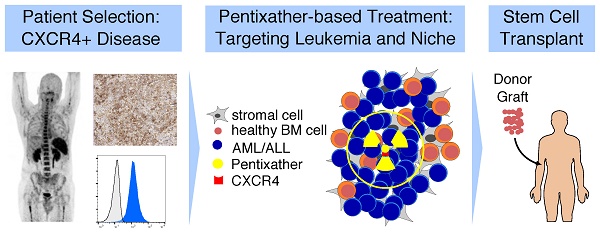
C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is a transmembrane receptor with pivotal roles in cell homing and hematopoiesis. CXCR4 is also involved in survival, proliferation and dissemination of cancer, including acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia (ALL, AML). Relapsed/refractory ALL and AML are frequently resistant to conventional therapy and novel highly active strategies are urgently needed to overcome resistance.
Methods: We used patient-derived (PDX) and cell line-based xenograft mouse models of ALL and AML to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of a CXCR4-targeted endoradiotherapy (ERT) theranostic approach.
Results: The positron emission tomography (PET) tracer 68Ga-Pentixafor enabled visualization of CXCR4 positive leukemic burden. In xenografts, CXCR4-directed ERT with 177Lu-Pentixather distributed to leukemia harboring organs and resulted in efficient reduction of leukemia. Despite a substantial in vivo cross-fire effect to the leukemia microenvironment, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) subjected to ERT were viable and capable of supporting the growth and differentiation of non-targeted normal hematopoietic cells ex vivo. Finally, three patients with refractory AML after first allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) underwent CXCR4-directed ERT resulting in leukemia clearance, second alloSCT, and successful hematopoietic engraftment.
Conclusion: Targeting CXCR4 with ERT is feasible and provides a highly efficient means to reduce refractory acute leukemia for subsequent cellular therapies. Prospective clinical trials testing the incorporation of CXCR4 targeting into conditioning regimens for alloSCT are highly warranted.
Keywords: acute leukemia, microenvironment, C-X-C chemokine receptor 4, in vivo molecular imaging, theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact