13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(4):972-989. doi:10.7150/thno.22328 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Homeotic Protein SIX3 Suppresses Carcinogenesis and Metastasis through Recruiting the LSD1/NuRD(MTA3) Complex
1. 2011 Collaborative Innovation Center of Tianjin for Medical Epigenetics, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Immunology, Key Laboratory of Immune Microenvironment and Disease (Ministry of Education), Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China;
2. Department of Biotherapy, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital; National Clinical Research Center for Cancer; Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy; Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer; Key Laboratory of Cancer Immunology and Biotherapy, Tianjin 300060, China.
Abstract
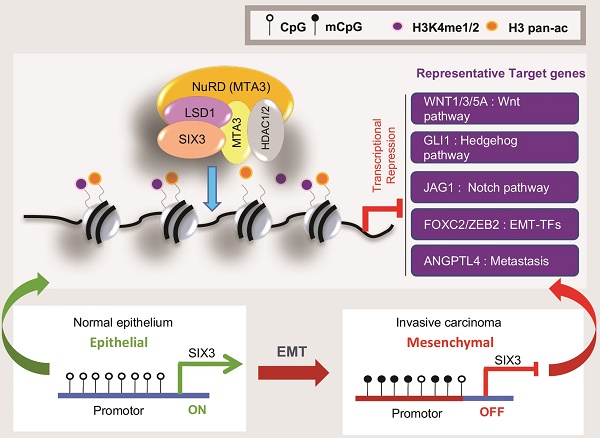
The homeodomain transcription factor SIX3 was recently reported to be a negative regulator of the Wnt pathway and has an emerging role in cancer. However, how SIX3 contributes to tumorigenesis and metastasis is poorly understood.
Methods: We employed affinity purification and mass spectrometry (MS) to identify the proteins physically associated with SIX3. Genome-wide analysis of the SIX3/LSD1/NuRD(MTA3) complex using a chromatin immunoprecipitation-on-chip approach identified a cohort of target genes including WNT1 and FOXC2, which are critically involved in cell proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Also, we used flow cytometry, growth curve analysis, EdU incorporation assay, colony formation assays, trans-well invasion assays, immunohistochemical staining and in vivo bioluminescence assay to investigate the function of SIX3 in tumorigenesis.
Results: We demonstrate that the SIX3/LSD1/NuRD(MTA3) complex inhibits carcinogenesis in breast cancer cells and suppresses metastasis in breast cancer. SIX3 expression is downregulated in various human cancers and high SIX3 is correlated with improved prognosis.
Conclusion: Our study revealed an important mechanistic link between the loss of function of SIX3 and tumor progression, identified a molecular basis for the opposing actions of MTA1 and MTA3, and may provide new potential prognostic indicators and targets for cancer therapy.
Keywords: epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, LSD1, MTA3, SIX3, tumorigenesis.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact