13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(10):2884-2895. doi:10.7150/thno.23824 This issue Cite
Research Paper
G9a stimulates CRC growth by inducing p53 Lys373 dimethylation-dependent activation of Plk1
1. Division of Anti-Tumor Pharmacology, State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201203, China;
2. School of life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China;
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Rationale: G9a is genetically deregulated in various tumor types and is important for cell proliferation; however, the mechanism underlying G9a-induced carcinogenesis, especially in colorectal cancer (CRC), is unclear. Here, we investigated if G9a exerts oncogenic effects in CRC by increasing polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) expression. Thus, we further characterized the detailed molecular mechanisms.
Methods: The role of Plk1 in G9a aberrant CRC was determined by performing different in vitro and in vivo assays, including assessment of cell growth by performing cell viability assay and assessment of signaling transduction profiles by performing immunoblotting, in the cases of pharmacological inhibition or short RNA interference-mediated suppression of G9a. Detailed molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of G9a on Plk1 expression were determined by performing point mutation analysis, chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis, and luciferase reporter assay. Correlation between G9a and Plk1 expression was determined by analyzing clinical samples of patients with CRC by performing immunohistochemistry.
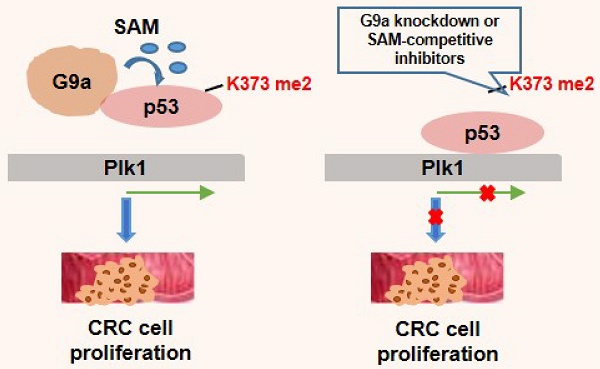
Results: Our study is the first to report a significant positive correlation between G9a and Plk1 levels in 89 clinical samples of patients with CRC. Moreover, G9a depletion decreased Plk1 expression and suppressed CRC cell growth both in vitro and in vivo, thus confirming the significant correlation between G9a and Plk1 levels. Further, we observed that G9a-induced Plk1 regulation depended on p53 inhibition. G9a dimethylated p53 at lysine 373, which in turn increased Plk1 expression and promoted CRC cell growth.
Conclusions: These results indicate that G9a-induced and p53-dependent epigenetic programing stimulates the growth of colon cancer, which also suggests that G9a inhibitors that restore p53 activity are promising therapeutic agents for treating colon cancer, especially for CRC expressing wild-type p53.
Keywords: G9a, polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), p53, colorectal cancer, proliferation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact