13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(12):3284-3307. doi:10.7150/thno.25220 This issue Cite
Review
Shape-, size- and structure-controlled synthesis and biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic theranostics
1. State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics and Fine Processing, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China.
2. Advanced Materials of Ministry of Education of China, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China.
3. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, 10083, China.
4. College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Northwest University, Xi'an, Shanxi 710069, China.
Abstract
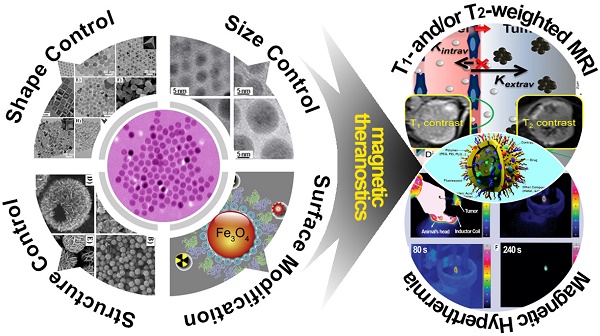
In the past decade, iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) have attracted more and more attention for their excellent physicochemical properties and promising biomedical applications. In this review, we summarize and highlight recent progress in the design, synthesis, biocompatibility evaluation and magnetic theranostic applications of IONPs, with a special focus on cancer treatment. Firstly, we provide an overview of the controlling synthesis strategies for fabricating zero-, one- and three-dimensional IONPs with different shapes, sizes and structures. Then, the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation and biotranslocation of IONPs are discussed in relation to their chemo-physical properties including particle size, surface properties, shape and structure. Finally, we also highlight significant achievements in magnetic theranostic applications including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic hyperthermia and targeted drug delivery. This review provides a background on the controlled synthesis, biocompatibility evaluation and applications of IONPs as cancer theranostic agents and an overview of the most up-to-date developments in this area.
Keywords: iron oxide, controlled synthesis, biocompatibility, magnetic theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact