13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(13):3693-3706. doi:10.7150/thno.24364 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Precise theranostic nanomedicines for inhibiting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque progression through regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching
1. Department of Cardiology & National Clinical Research Center of Geriatrics Disease, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China.
3. Laboratory of Controllable Nanopharmaceuticals, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Center for Excellence in Nanoscience and CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology of China, Beijing 100190, China.
4. Department of Emergency Medicine, Jinling Hospital, Nanjing 210000, China.
5. State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Disease and Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China.
6. Department of Geriatric Cardiology & National Clinical Research Center of Geriatric Disease, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
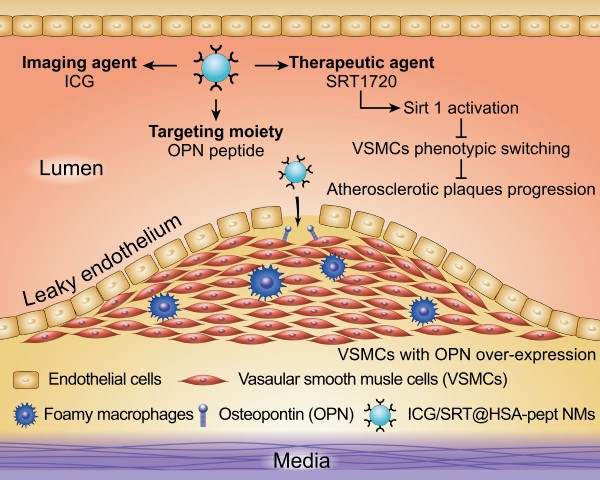
Coronary heart disease is a prevalent and fatal killer caused by vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques (VASPs). However, the precise detection and treatment of VASPs remains a difficult challenge. Here, we present the development of noninvasive human serum albumin (HSA)-based theranostic nanomedicines (NMs) for the specific diagnosis and effective therapy of VASPs.
Methods: The ICG/SRT@HSA-pept NMs were formulated to contain payloads of the near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent dye indocyanine green (ICG) and the sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) activator SRT1720, and modified with a peptide moiety targeting osteopontin (OPN). The in vivo atherosclerotic mouse model was established with the high-fat diet (HFD). The in vitro vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) phenotypic switching was induced using the ox-LDL stimulation.
Results: Due to the overexpression of OPN in activated VSMCs and VASPs, the targeted NMs specifically accumulated within the VASPs region after intravenous injection into the atherosclerotic mice, achieving the precise detection of VASPs. In addition, in the presence of SRT1720, the NMs could activate intracellular Sirt1 and activate an antiatherogenesis effect by inhibiting the phenotypic switching of VSMCs, which is an essential contributor to the vulnerability and progression of atherosclerotic plaques. After therapeutic administration of the ICG/SRT@HSA-pept NMs for two weeks, the physiological sizes and plaque compositions of VASPs were markedly improved. Furthermore, ICG/SRT@HSA-pept NMs-treated mice presented a more favorable plaque phenotype than that was observed in free SRT1720-treated mice, suggesting the enhanced delivery of pharmaceutical agents to the atherosclerotic lesions and improved therapeutic efficacy of NMs compared with free SRT1720.
Conclusions: The theranostic ICG/SRT@HSA-pept NMs showed great potential for the precise identification and targeted treatment of atherosclerotic diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, theranostic nanomedicines, sirtuin 1, osteopontin, vascular smooth muscle cells
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact