13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(14):3891-3901. doi:10.7150/thno.24056 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tumor-suppressing miR-141 gene complex-loaded tissue-adhesive glue for the locoregional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
1. World Class Smart Lab, Department of New Drug Development, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Molecular Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Republic of Korea
*The authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
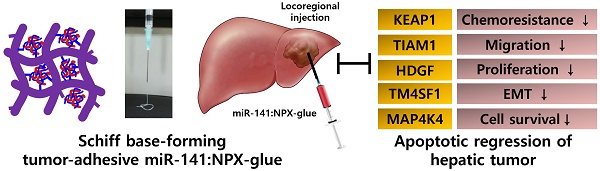
microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally and have been extensively tested as therapeutic molecules against several human diseases. In vivo delivery of miRNAs needs to satisfy the following conditions: safety, efficiency, and long-term therapeutic effectiveness. To satisfy these conditions, we developed a tissue-adhesive nucleotide-polymer complex (NPX-glue) for in vivo delivery of miRNAs to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Polyallylamine (PAA), a cationic polymer, was mixed with tumor-suppressing miR-141 to form NPX and then mixed with partially oxidized alginate (OA) to form NPX-glue. Delivery efficiency of miR-141:NPX-glue was determined in cultured HCC cells and in an implanted HCC tumor model. In vivo tumor-suppressive effects of miR-141 on HCC were examined in mice upon intratumoral injection of miR-141:NPX-glue.
Result: NPX-glue was generated by mixing of NPX with OA, which eliminated the inherent cytotoxic effect of NPX. NPX-glue led to the efficient delivery of miR-141 and plasmid to cultured cells and solid tumors in mice, where their expression was maintained for up to 30 days. Upon intratumoral injection of miR-141:NPX-glue, the growth of the tumors was dramatically retarded in comparison with the negative control, NCmiR:NPX-glue, (p < 0.05). Molecular examination proved miR-141:NPX-glue efficiently regulated the target genes including MAP4K4, TM4SF1, KEAP1, HDGF, and TIAM1 and finally induced apoptosis of cancer tissues.
Conclusion: Here, we show that NPX-glue delivers therapeutic miR-141 to solid tumors in a safe, stable, and long-term manner and prove that locoregional treatment of HCC is possible using the NPX-glue system.
Keywords: miR-141, nucleotide complex, tissue adhesive glue, hepatic cancer, gene delivery
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact