13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(8):3474-3487. doi:10.7150/thno.39434 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tumor cell-derived exosomes home to their cells of origin and can be used as Trojan horses to deliver cancer drugs
1. Department of Molecular Biomedical Science, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA.
2. Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, and North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA.
3. Department of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China.
4. Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China.
5. Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China.
Abstract
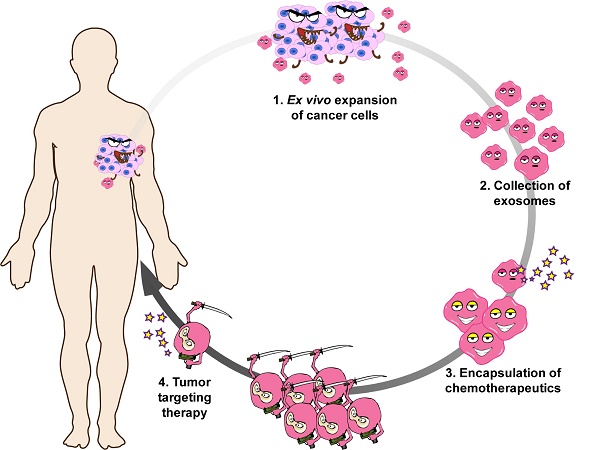
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide and patients are in urgent need of therapies that can effectively target cancer with minimal off-target side effects. Exosomes are extracellular nano-shuttles that facilitate intercellular communication between cells and organs. It has been established that tumor-derived exosomes contain a similar protein and lipid composition to that of the cells that secrete them, indicating that exosomes might be uniquely employed as carriers for anti-cancer therapeutics.
Methods: We isolated exosomes from two cancer cell lines, then co-cultured each type of cancer cells with these two kinds of exosomes and quantified exosome. HT1080 or Hela exosomes were systemically injected to Nude mice bearing a subcutaneous HT1080 tumor to investigate their cancer-homing behavior. Moreover, cancer cell-derived exosomes were engineered to carry Doxil (a common chemotherapy drug), known as D-exo, were used to detect their target and therapeutic efficacy as anti-cancer drugs. Exosome proteome array analysis were used to reveal the mechanism underly this phenomenon.
Results: Exosomes derived from cancer cells fuse preferentially with their parent cancer cells, in vitro. Systemically injected tumor-derived exosomes home to their original tumor tissues. Moreover, compared to Doxil alone, the drug-loaded exosomes showed enhanced therapeutic retention in tumor tissues and eradicated them more effectively in nude mice. Exosome proteome array analysis revealed distinct integrin expression patterns, which might shed light on the underlying mechanisms that explain the exosomal cancer-homing behavior.
Conclusion: Here we demonstrate that the exosomes' ability to target the parent cancer is a phenomenon that opens up new ways to devise targeted therapies to deliver anti-tumor drugs.
Keywords: exosome, homing, integrin, doxorubicin, cancer therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact