13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(4):1311-1324. doi:10.7150/thno.79326 This issue Cite
Research Paper
WT1+ glomerular parietal epithelial progenitors promote renal proximal tubule regeneration after severe acute kidney injury
1. Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
3. National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Guangzhou, China
4. Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Kidney Disease, Guangzhou, China
5. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Renal Failure Research, Guangzhou, China
6. Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, 510005 Guangzhou, China
7. East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China
8. Kiangnan Stem Cell Institute, Zhejiang 311300, China
9. Division of Nephrology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, No.88, Jiefang Road, Shangcheng District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310009, China
* Lead contact
# These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
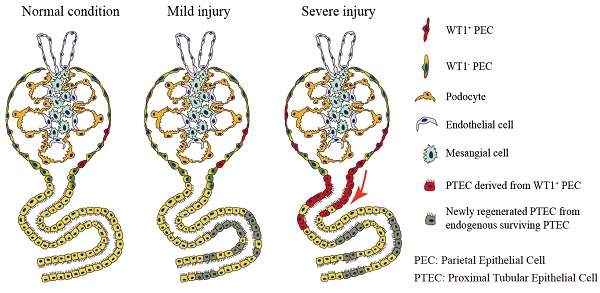
Rationale: Mammalian renal proximal tubules can partially regenerate after acute kidney injury (AKI). However, cells participating in the renal proximal tubule regeneration remain to be elucidated. Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1) expresses in a subtype of glomeruli parietal epithelial cells (PECs) in adult kidneys, it remains unclear whether these WT1+ PECs play a role in renal regeneration/repair after AKI.
Methods: Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) mouse model was used to investigate the expression pattern of WT1 in the kidney after severe AKI. Conditional deletion of WT1 gene mice were generated using Pax8CreERT2 and WT1fl/fl mice to examine the function of WT1. Then, genetic cell lineage tracing and single-cell RNA sequencing were performed to illustrate that WT1+ PECs develop into WT1+ proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs). Furthermore, in vitro clonogenicity, direct differentiation analysis and in vivo transplantation were used to reveal the stem cell-like properties of these WT1+ PECs.
Results: The expression of WT1 protein in PECs and PTECs was increased after severe AKI. Conditional deletion of WT1 gene in PTECs and PECs aggravated renal tubular injury after severe AKI. WT1+ PECs develop into WT1+ PTECs via the transient scattered tubular cell stage, and these WT1+ PECs possess specific stem cell-like properties.
Conclusions: We discovered a group of WT1+ PECs that promote renal proximal tubule regeneration/repair after severe AKI, and the expression of WT1 in PECs and PTECs is essential for renal proximal tubule regeneration after severe kidney injury.
Keywords: WT1, parietal epithelial cells, renal progenitors, regeneration, acute kidney injury
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact