13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(11):3655-3674. doi:10.7150/thno.85823 This issue Cite
Review
LncRNAs associated with oxidative stress in diabetic wound healing: Regulatory mechanisms and application prospects
1. Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education, Drug Discovery Research Center, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China.
2. Laboratory for Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China.
3. Luzhou Municipal Key Laboratory of Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, Luzhou, Sichuan, China.
4. Department of General Surgery (Thyroid Surgery), the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China.
5. Metabolic Vascular Diseases Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Luzhou, Sichuan, China.
6. Department of Pharmacy, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China.
# Qinzhi Yang and Dan Fang have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
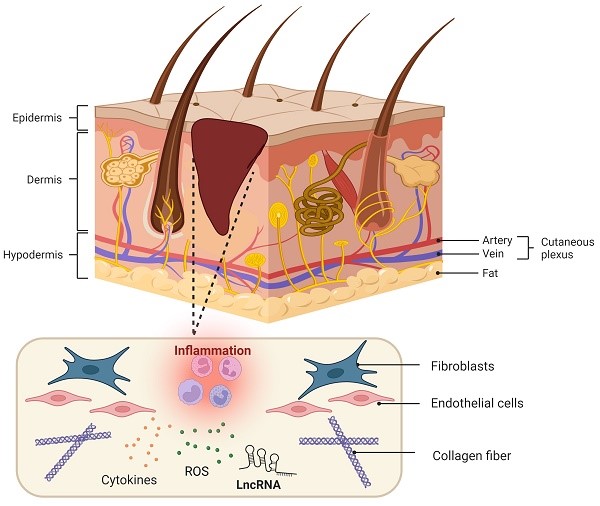
Diabetes is a group of chronic diseases with blood glucose imbalance, and long-term hyperglycaemia causes sustained damage to various organs of the body, resulting in vascular lesions, neuropathy and impaired wound healing. Diabetic wound formation involves a variety of complex mechanisms, and they are characterized by a persistent chronic inflammatory response, degradation of angiogenesis and imbalance of extracellular matrix regulation, all of which are related to oxidative stress. Additionally, repair and healing of diabetic wounds require the participation of a variety of cells, cytokines, genes, and other factors, which together constitute a complex biological regulatory network. Recent studies have shown that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) can be involved in the regulation of several key biological pathways and cellular functions demonstrating their critical role in diabetic wound healing. LncRNAs are a major family of RNAs with limited or no protein-coding function. Numerous studies have recently reported a strong link between oxidative stress and lncRNAs. Given that both lncRNAs and oxidative stress have been identified as potential drivers of diabetic wound healing, their link in diabetic wound healing can be inferred. However, the specific mechanism of oxidative stress related to lncRNAs in diabetic wound healing is still unclear, and elucidating the functions of lncRNAs in these processes remains a major challenge. This article reviews the mechanisms of lncRNAs related to oxidative stress in several stages of diabetic wound healing and discusses diagnostic and treatment potential of lncRNAs to treat diabetic wounds by improving oxidative stress, as well as the challenges of using lncRNAs for this purpose. It is hoped that these results will provide new targets and strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of impaired wound healing in diabetic patients.
Keywords: diabetes, wound healing, oxidative stress, lncRNAs, therapeutic application
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact