13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(11):3761-3780. doi:10.7150/thno.83676 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sufu limits sepsis-induced lung inflammation via regulating phase separation of TRAF6
1. College of Life Sciences, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730070, P. R. China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, P. R. China.
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, P. R. China.
4. Center for Clinical Research and Translational Medicine, Yangpu Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200090, P. R. China.
5. State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, School of Life Sciences, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200438, P. R. China.
6. Department of Medical Ultrasound, Tongji University Cancer Center, Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital, Shanghai 200072, P. R. China.
7. School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, P. R. China.
8. Key Laboratory of Systems Health Science of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, P. R. China
# These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
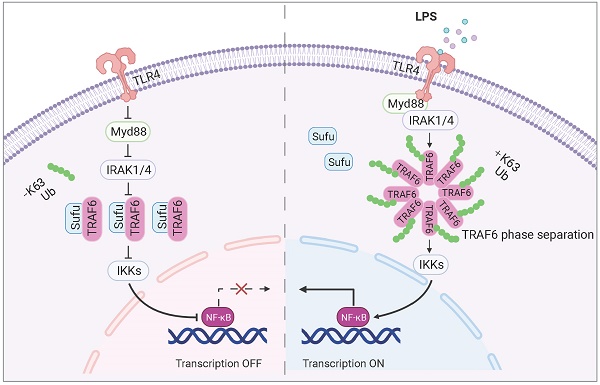
Rationale: Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to a severe infection. Although the identification of multiple pathways involved in inflammation, tissue damage and aberrant healing during sepsis, there remain unmet needs for the development of new therapeutic strategies essential to prevent the reoccurrence of infection and organ injuries.
Methods: Expression of Suppressor of Fused (Sufu) was evaluated by qRT-PCR, western blotting, and immunofluorescence in murine lung and peritoneal macrophages. The significance of Sufu expression in prognosis was assessed by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. The GFP-TRAF6-expressing stable cell line (GFP-TRAF6 Blue cells) were constructed to evaluate phase separation of TRAF6. Phase separation of TRAF6 and the roles of Sufu in repressing TRAF6 droplet aggregation were analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, Native-PAGE, FRAP and in vitro assays using purified proteins. The effects of Sufu on sepsis-induced lung inflammation were evaluated by cell function assays, LPS-induced septic shock model and polymicrobial sepsis-CLP mice model.
Results: We found that Sufu expression is reduced in early response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute inflammation in murine lung and peritoneal macrophages. Deletion of Sufu aggravated LPS-induced and CLP (cecal ligation puncture)-induced lung injury and lethality in mice, and augmented LPS-induced proinflammatory gene expression in cultured macrophages. In addition, we identified the role of Sufu as a negative regulator of the Toll-Like Receptor (TLR)-triggered inflammatory response. We further demonstrated that Sufu directly interacts with TRAF6, thereby preventing oligomerization and autoubiquitination of TRAF6. Importantly, TRAF6 underwent phase separation during LPS-induced inflammation, which is essential for subsequent ubiquitination activation and NF-κB activity. Sufu inhibits the phase-separated TRAF6 droplet formation, preventing NF-κB activation upon LPS stimulation. In a septic shock model, TRAF6 depletion rescued the augmented inflammatory phenotype in mice with myeloid cell-specific deletion of Sufu.
Conclusions: These findings implicated Sufu as an important inhibitor of TRAF6 in sepsis and suggest that therapeutics targeting Sufu-TRAF6 may greatly benefit the treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: Sufu, TRAF6, Sepsis, Phase separation, inflammatory response
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact