13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(11):3844-3855. doi:10.7150/thno.83819 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A de novo dual-targeting supramolecular self-assembly peptide against pulmonary metastasis of melanoma
1. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
2. Institute for Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710004, China.
3. Department of Talent Highland, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an 710061, China.
† These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
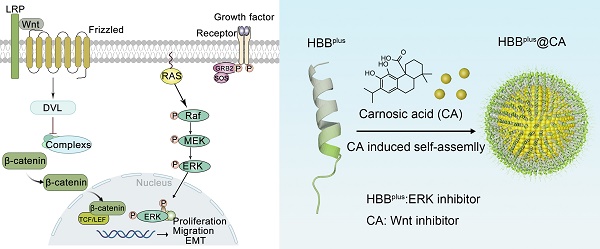
Despite recent advances in treatment, overall survival rates for metastatic melanoma, especially those that invade the lungs, continue to be low, with 5-year survival rates of only 3% to 5%. It was recently discovered that Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways are involved in melanoma metastasis.
Methods: Herein, a bifunctional supramolecular peptide termed HBBplus@CA was constructed by a self-assembling RGD-modified MAPK/ERK peptide inhibitor (HBBplus) and a small molecule catenin inhibitor (carnosic acid (CA)).
Results: Expectedly, the HBBplus@CA could internalize melanoma cells, accumulate in the tumor-bearing lung, and be biosafe. As designed, HBBplus@CA simultaneously suppressed both Wnt/β-catenin and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways and suppressed melanoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in more action than CA or HBBplus monotherapy. More importantly, HBBplus@CA demonstrated potent inhibition of lung metastasis in mice bearing metastatic melanoma of B16F10 and significantly prolonged their survival.
Conclusion: In summary, a supramolecular peptide-based strategy was not only developed to suppress pulmonary metastasis of melanoma, but it also renewed efforts to identify cocktail drugs that act on intracellular targets in various human diseases, including cancer.
Keywords: Peptide, Wnt/β-catenin, Supramolecular self-assembly, Melanoma metastasis, Cancer therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact