13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(14):4872-4884. doi:10.7150/thno.86831 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting redox imbalance in neurodegeneration: characterizing the role of GLP-1 receptor agonists
1. Department of Advanced Medical and Surgical Sciences, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Naples, Italy.
2. IRCCS MultiMedica, Milan, Italy.
3. UniCamillus, International Medical University, Rome Italy.
#Contributed equally.
Abstract
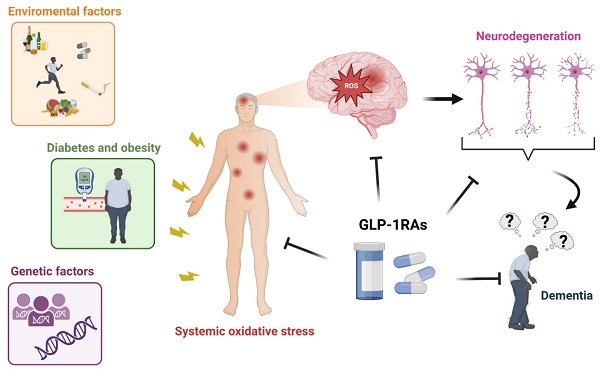
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have emerged as essential signaling molecules regulating cell survival, death, inflammation, differentiation, growth, and immune response. Environmental factors, genetic factors, or many pathological condition such as diabetes increase the level of ROS generation by elevating the production of advanced glycation end products, reducing free radical scavengers, increasing mitochondrial oxidative stress, and by interfering with DAG-PKC-NADPH oxidase and xanthine oxidase pathways. Oxidative stress, and therefore the accumulation of intracellular ROS, determines the deregulation of several proteins and caspases, damages DNA and RNA, and interferes with normal neuronal function. Furthermore, ROS play an essential role in the polymerization, phosphorylation, and aggregation of tau and amyloid-beta, key mediators of cognitive function decline. At the neuronal level, ROS interfere with the DNA methylation pattern and various apoptotic factors related to cell death, promoting neurodegeneration. Only few drugs are able to quench ROS production in neurons. The cross-linking pathways between diabetes and dementia suggest that antidiabetic medications can potentially treat dementia. Among antidiabetic drugs, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been found to reduce ROS generation and ameliorate mitochondrial function, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. The incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is produced by the enteroendocrine L cells in the distal intestine after food ingestion. Upon interacting with its receptor (GLP-1R), it regulates blood glucose levels by inducing insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon production, and slowing gastric emptying. No study has evidenced a specific GLP-1RA pathway that quenches ROS production. Here we summarize the effects of GLP-1RAs against ROS overproduction and discuss the putative efficacy of Exendin-4, Lixisenatide, and Liraglutide in treating dementia by decreasing ROS.
Keywords: ROS, Dementia, Diabetes, GLP-1RAs, Oxidative stress
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact