13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(14):5017-5056. doi:10.7150/thno.78876 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting cullin neddylation for cancer and fibrotic diseases
1. Pharmacy College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, 450046, Zhengzhou, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Esophageal Cancer Prevention and Treatment; Key Laboratory of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology, Ministry of Education of China; School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450001, China.
3. Children's hospital affiliated of Zhengzhou university; Henan children's hospital; Zhengzhou children's hospital, Henan Zhengzhou 450000, China.
4. China Meheco Topfond Pharmaceutical Co., Zhumadian 463000, China.
5. Key Laboratory of Cardio-cerebrovascular Drug, Henan Province, Zhumadian 463000, China.
#: These authors contribute equally to this work.
*: These senior authors contribute equally to this work.
Abstract
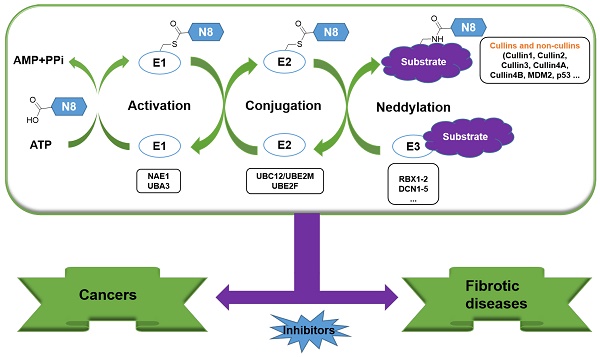
Protein neddylation is a post-translational modification, and its best recognized substrates are cullin family proteins, which are the core component of Cullin-RING ligases (CRLs). Given that most neddylation pathway proteins are overactivated in different cancers and fibrotic diseases, targeting neddylation becomes an emerging approach for the treatment of these diseases. To date, numerous neddylation inhibitors have been developed, of which MLN4924 has entered phase I/II/III clinical trials for cancer treatment, such as acute myeloid leukemia, melanoma, lymphoma and solid tumors. Here, we systematically describe the structures and biological functions of the critical enzymes in neddylation, highlight the medicinal chemistry advances in the development of neddylation inhibitors and propose the perspectives concerning targeting neddylation for cancer and fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: Cullin neddylation, Inhibitors, Cancer, Fibrotic diseases
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact