13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):1-16. doi:10.7150/thno.89913 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Bile acid-containing lipid nanoparticles enhance extrahepatic mRNA delivery
1. Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
2. Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
3. Abramson Cancer Center, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
4. Institute for Immunology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
5. Cardiovascular Institute, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
6. Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
7. Penn Institute for RNA Innovation, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
Abstract
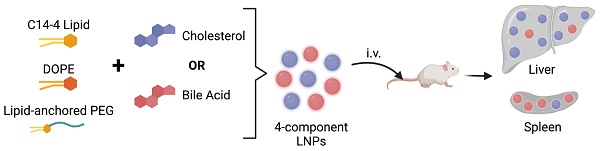
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a viable, clinically-validated platform for the delivery of mRNA therapeutics. LNPs have been utilized as mRNA delivery systems for applications including vaccines, gene therapy, and cancer immunotherapy. However, LNPs, which are typically composed of ionizable lipids, cholesterol, helper lipids, and lipid-anchored polyethylene glycol, often traffic to the liver which limits the therapeutic potential of the platform. Several approaches have been proposed to resolve this tropism such as post-synthesis surface modification or the addition of synthetic cationic lipids.
Methods: Here, we present a strategy for achieving extrahepatic delivery of mRNA involving the incorporation of bile acids, a naturally-occurring class of cholesterol analogs, during LNP synthesis. We synthesized a series of bile acid-containing C14-4 LNPs by replacing cholesterol with bile acids (cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid, deoxycholic acid, or lithocholic acid) at various ratios.
Results: Bile acid-containing LNPs (BA-LNPs) were able to reduce delivery to liver cells in vitro and improve delivery in a variety of other cell types, including T cells, B cells, and epithelial cells. Our subsequent in vivo screening of selected LNP candidates injected intraperitoneally or intravenously identified a highly spleen tropic BA-LNP: CA-100, a four-component LNP containing cholic acid and no cholesterol. These screens also identified BA-LNP candidates demonstrating promise for other mRNA therapeutic applications such as for gastrointestinal or immune cell delivery. We further found that the substitution of cholic acid for cholesterol in an LNP formulation utilizing a different ionizable lipid, C12-200, also shifted mRNA delivery from the liver to the spleen, suggesting that this cholic acid replacement strategy may be generalizable.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the potential of a four-component BA-LNP formulation, CA-100, for extrahepatic mRNA delivery that could potentially be utilized for a range of therapeutic and vaccine applications.
Keywords: lipid nanoparticles, extrahepatic delivery, mRNA
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact