13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(3):1029-1048. doi:10.7150/thno.92449 This issue Cite
Review
Antibacterial micro/nanomotors: current research progress, challenges, and opportunities
1. State Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine Ministry of Education, Hubei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, School & Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University.
2. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University, 430079 Wuhan, China.
Abstract
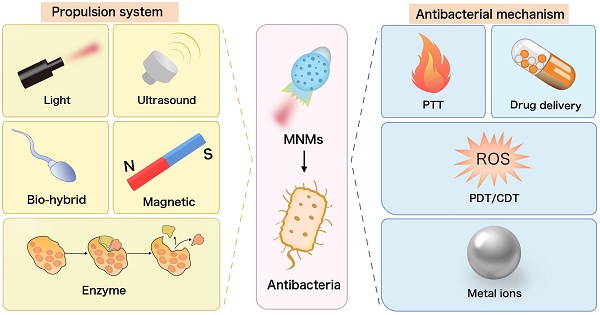
Bacterial infections remain a formidable threat to human health, a situation exacerbated by the escalating problem of antibiotic resistance. While alternative antibacterial strategies such as oxidants, heat treatments, and metal nanoparticles (NPs) have shown potential, they come with significant drawbacks, ranging from non-specificity to potential environmental concerns. In the face of these challenges, the rapid evolution of micro/nanomotors (MNMs) stands out as a revolutionary development in the antimicrobial arena. MNMs harness various forms of energy and convert it into a substantial driving force, offering bright prospects for combating microbial threats. MNMs' mobility allows for swift and targeted interaction with bacteria, which not only improves the carrying potential of therapeutic agents but also narrows the required activation range for non-drug antimicrobial interventions like photothermal and photodynamic therapies, substantially improving their bacterial clearance rates. In this review, we summarized the diverse propulsion mechanisms of MNMs employed in antimicrobial applications and articulated their multiple functions, which include direct bactericidal action, capture and removal of microorganisms, detoxification processes, and the innovative detection of bacteria and associated toxins. Despite MNMs' potential to revolutionize antibacterial research, the translation from laboratory to clinical use remains challenging. Based on the current research status, we summarized the potential challenges and possible solutions and also prospected several key directions for future studies of MNMs for antimicrobial purposes. Collectively, by highlighting the important knowns and unknowns of antimicrobial MNMs, our present review would help to light the way forward for the field of antimicrobial MNMs and prevent unnecessary blindness and detours.
Keywords: micro/nanomotors, bacterial infections, challenges, opportunities
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact