13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(4):1325-1343. doi:10.7150/thno.90779 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Therapeutic effects of a novel electrode for transcranial direct current stimulation in ischemic stroke mice
1. Department of Korean Medical Science, School of Korean Medicine, Pusan National University, Yangsan 50612, Republic of Korea.
2. Graduate Training Program of Korean Medical Therapeutics for Healthy Aging, Pusan National University, Yangsan 50612, Republic of Korea.
3. Korea Radioisotope Center for Pharmaceuticals, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Republic of Korea.
4. School of Healthcare and Biomedical Engineering, Chonnam National University, Yeosu 59626, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
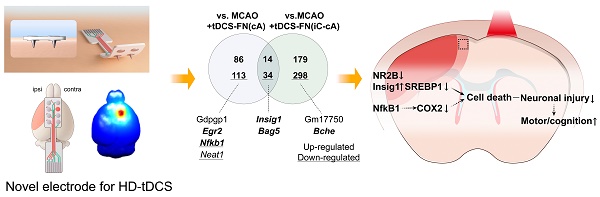
Rationale: Non-invasive transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a promising stimulation tool to modulate a wide range of brain disorders, has major limitations, such as poor cortical stimulation intensity and focality. We designed a novel electrode for tDCS by conjugating a needle to a conventional ring-based high-definition (HD) electrode to enhance cortical stimulation efficacy.
Method: HD-tDCS (43 µA/mm2, charge density 51.6 kC/m2, 20 min) was administered to male C57BL/6J mice subjected to early-stage ischemic stroke. Behavioral tests were employed to determine the therapeutic effects, and the underlying mechanisms of HD-tDCS were determined by performing RNA sequencing and other biomedical analyses.
Results: The new HD-tDCS application, showing a higher electric potential and spatial focality based on computational modeling, demonstrated better therapeutic effects than conventional HD-tDCS in alleviating motor and cognitive deficits, with a decrease in infarct volume and inflammatory response. We assessed different electrode configurations in the new HD electrode; the configurations variously showed potent therapeutic effects, ameliorating neuronal death in the peri-infarct region via N-methyl-D-aspartate-dependent sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 signaling and related inflammatory factors, further alleviating motor and cognitive deficits in stroke.
Conclusion: This new HD-tDCS application showed better therapeutic effects than those with conventional HD-tDCS in early-stage stroke via the amelioration of neuronal death in the penumbra. It may be applied in the early stages of stroke to alleviate neurological impairment.
Keywords: Transcranial direct current stimulation, High-definition electrode, Stroke, RNA sequencing, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact