13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(4):1781-1793. doi:10.7150/thno.91165 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Activatable prodrug for controlled release of an antimicrobial peptide via the proteases overexpressed in Candida albicans and Porphyromonas gingivalis
1. Program in Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, United States.
2. Department of NanoEngineering, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, United States.
3. Department of Radiology, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, United States.
Abstract
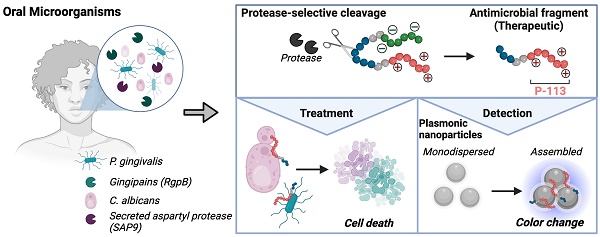
Candida albicans and Porphyromonas gingivalis are prevalent in the subgingival area where the frequency of fungal colonization increases with periodontal disease. Candida's transition to a pathogenic state and its interaction with P. gingivalis exacerbate periodontal disease severity. However, current treatments for these infections differ, and combined therapy remains unexplored. This work is based on an antimicrobial peptide that is therapeutic and induces a color change in a nanoparticle reporter.
Methods: We built and characterized two enzyme-activatable prodrugs to treat and detect C. albicans and P. gingivalis via the controlled release of the antimicrobial peptide. The zwitterionic prodrug quenches the antimicrobial peptide's activity until activation by a protease inherent to the pathogens (SAP9 for C. albicans and RgpB for P. gingivalis). The toxicity of the intact prodrugs was evaluated against fungal, bacterial, and mammalian cells. Therapeutic efficacy was assessed through microscopy, disk diffusion, and viability assays, comparing the prodrug to the antimicrobial peptide alone. Finally, we developed a colorimetric detection system based on the aggregation of plasmonic nanoparticles.
Results: The intact prodrugs showed negligible toxicity to cells absent a protease trigger. The therapeutic impact of the prodrugs was comparable to that of the antimicrobial peptide alone, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 3.1 - 16 µg/mL. The enzymatic detection system returned a detection limit of 10 nM with gold nanoparticles and 3 nM with silver nanoparticles.
Conclusion: This approach offers a convenient and selective protease sensing and protease-induced treatment mechanism based on bioinspired antimicrobial peptides.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides, plasmonic nanoparticles, oral microorganisms, controlled assembly, protease sensing
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact