13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(5):2265-2289. doi:10.7150/thno.93115 This issue Cite
Review
Extracellular vesicles as carriers of mRNA: Opportunities and challenges in diagnosis and treatment
1. Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 20742
2. Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Maryland Health Care System, Baltimore, MD, USA
3. Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 20742
4. Robert E. Fischell Institute for Biomedical Devices, College Park, MD 20742, USA
5. Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 21201
* Authors contributed equally
Abstract
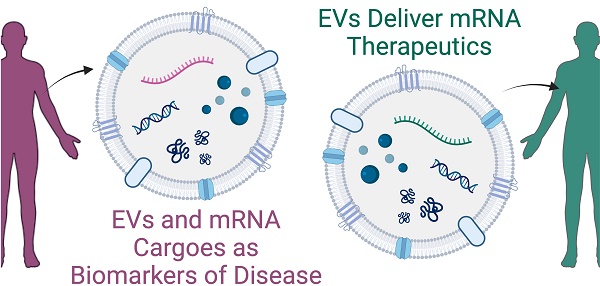
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are produced by all cells in the body. These biological nanoparticles facilitate cellular communication through the transport of diverse cargoes, including small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids. mRNA cargoes have gained particular interest given their role in the translation of functional proteins. As a biomarker platform, EVs can be found in nearly all biofluids—blood, mucus, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and saliva—providing real-time insight into parent cell and tissue function. mRNAs carried by EVs are protected from degradation, resulting in improved detection compared to free mRNA, and recent work demonstrates promising results in using these mRNA cargoes as biomarkers for cancer, neurological diseases, infectious diseases, and gynecologic and obstetric outcomes. Furthermore, given the innate cargo carrying, targeting, and barrier crossing abilities of EVs, these structures have been proposed as therapeutic carriers of mRNA. Recent advances demonstrate methods for loading mRNAs into EVs for a range of disease indications. Here, we review recent studies using EVs and their mRNA cargoes as diagnostics and therapeutics. We discuss challenges associated with EVs in diagnostic and therapeutic applications and highlight opportunities for future development.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, biomarkers, mRNA delivery, vaccines, therapeutics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact