13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(7):2816-2834. doi:10.7150/thno.93256 This issue Cite
Research Paper
In situ single-cell therapeutic response imaging facilitated by the TRIPODD fluorescence imaging platform
1. Biomedical Engineering Department, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR 97201, USA.
2. Knight Cancer Institute, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR 97201, USA.
3. Thayer School of Engineering, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH 03755, USA.
4. Geisel School of Medicine, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH 03755, USA.
5. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL 60616, USA.
Abstract
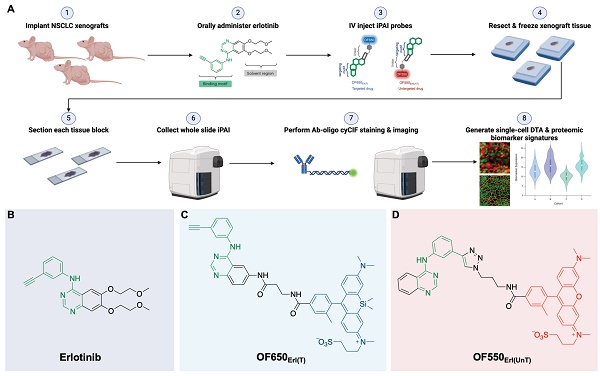
Purpose: Small molecule drugs such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting tumoral molecular dependencies have become standard of care for numerous cancer types. Notably, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) TKIs (e.g., erlotinib, afatinib, osimertinib) are the current first-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) due to their improved therapeutic outcomes for EGFR mutated and overexpressing disease over traditional platinum-based chemotherapy. However, many NSCLC tumors develop resistance to EGFR TKI therapy causing disease progression. Currently, the relationship between in situ drug target availability (DTA), local protein expression and therapeutic response cannot be accurately assessed using existing analytical tools despite being crucial to understanding the mechanism of therapeutic efficacy.
Procedure: We have previously reported development of our fluorescence imaging platform termed TRIPODD (Therapeutic Response Imaging through Proteomic and Optical Drug Distribution) that is capable of simultaneous quantification of single-cell DTA and protein expression with preserved spatial context within a tumor. TRIPODD combines two complementary fluorescence imaging techniques: intracellular paired agent imaging (iPAI) to measure DTA and cyclic immunofluorescence (cyCIF), which utilizes oligonucleotide conjugated antibodies (Ab-oligos) for spatial proteomic expression profiling on tissue samples. Herein, TRIPODD was modified and optimized to provide a downstream analysis of therapeutic response through single-cell DTA and proteomic response imaging.
Results: We successfully performed sequential imaging of iPAI and cyCIF resulting in high dimensional imaging and biomarker assessment to quantify single-cell DTA and local protein expression on erlotinib treated NSCLC models. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies of the erlotinib iPAI probes revealed that administration of 2.5 mg/kg each of the targeted and untargeted probe 4 h prior to tumor collection enabled calculation of DTA values with high Pearson correlation to EGFR, the erlotinib molecular target, expression in the tumors. Analysis of single-cell biomarker expression revealed that a single erlotinib dose was insufficient to enact a measurable decrease in the EGFR signaling cascade protein expression, where only the DTA metric detected the presence of bound erlotinib.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the capability of TRIPODD to evaluate therapeutic response imaging to erlotinib treatment as it relates to signaling inhibition, DTA, proliferation, and apoptosis with preserved spatial context.
Keywords: intracellular paired agent imaging, fluorescence imaging, drug target availability, cyclic immunofluorescence, cancer heterogeneity
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact