13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(9):1353-1361. doi:10.7150/thno.16093 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Accurate Quantification of Disease Markers in Human Serum Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-linked Immunosorbent Assay
1. Department of Bioengineering, Rice University, Houston, TX 77005, USA.
2. State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China;
3. Institute of Biomedical Sciences, College of Life Sciences, Key Laboratory of Animal Resistance of Shandong Province, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes of the Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
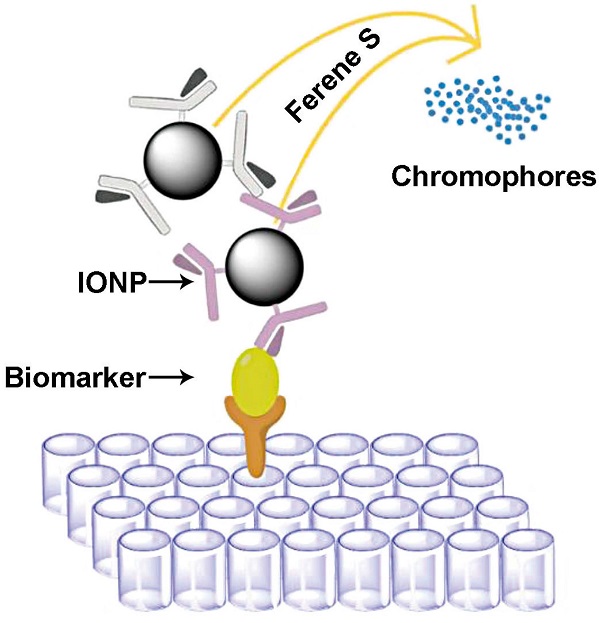
Accurate and reliable quantification of biomarkers in the blood is essential in disease screening and diagnosis. Here we describe an iron oxide nanoparticle (IONP)-linked immunosorbent assay (ILISA) for detecting biomolecules in human serum. Sandwich ILISA was optimized for the detection of four important serological markers, IgA, IgG, IgM, and C-reactive protein (CRP), and assessed with normal sera, simulated disease-state sera and the serum samples from patients infected with West Nile virus (WNV) or human herpes virus (HHV). Our study shows that using the detection assay formulated with 18.8 nm wüstite nanocrystals, ILISA can achieve sub-picomolar detection sensitivity, and all four markers can be accurately quantified over a large dynamic range. In addition, ILISA is not susceptible to variations in operating procedures and shows better linearity and higher stability compared with ELISA, which facilitates its integration into detection methods suitable for point of care. Our results demonstrate that ILISA is a simple and versatile nanoplatform for highly sensitive and reliable detection of serological biomarkers in biomedical research and clinical applications.
Keywords: iron oxide nanoparticle, immunosorbent assay, serological biomarker, quantification.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact