13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(17):4959-4970. doi:10.7150/thno.35366 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Sex modulates the ApoE ε4 effect on brain tau deposition measured by 18F-AV-1451 PET in individuals with mild cognitive impairment
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
2. The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States of America
3. Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States of America
4. Department of Neurology, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, United States of America
5. Medical Scientist Training Program, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, United States of America
6. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, United States of America
7. Department of Radiology, Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
The strongest genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the Apolipoprotein E type 4 allele (ApoE ε4). The interaction between sex and ApoE ε4 carrier status on AD risk remains an area of intense investigation. We hypothesized that sex modulates the relationship between ApoE ε4 carrier status and brain tau deposition (a quantitative endophenotype in AD) in individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Methods: Preprocessed 18F-AV-1451 tau and 18F-AV-45 amyloid PET images, T1-weighted structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, demographic information, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) total tau (t-tau) and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) measurements from 108 MCI subjects in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database were included. After downloading pre-processed images from ADNI, an iterative reblurred Van Cittertiteration partial volume correction (PVC) method was applied to all PET images. MRIs were used for PET spatial normalization. Regions of interest (ROIs) were defined in standard space, and standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) images relative to cerebellum were computed. ApoE ε4 by sex interaction analyses on 18F-AV-1451 and CSF tau (t-tau, p-tau) were assessed using generalized linear models. The association between 18F-AV-1451 SUVR and CSF tau (t-tau, p-tau) was assessed.
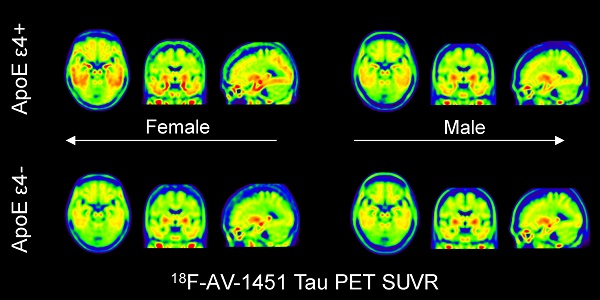
Results: After applying PVC and controlling for age, education level and global cortical 18F-AV-45 SUVR, we found that the entorhinal cortex, amygdala, parahippocampal gyrus, posterior cingulate, and occipital ROIs exhibited a significant ApoE ε4 by sex interaction effect (false discovery rate P < 0.1) among MCI individuals. We also found a significant ApoE ε4 by sex interaction effect on CSF t-tau and p-tau. 18F-AV-1451 SUVR in the 5 ROIs with ApoE ε4 by sex interaction was significantly correlated with CSF p-tau and t-tau.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that women are more susceptible to ApoE ε4-associated accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles in MCI compared to males. Both CSF tau (p-tau, t-tau) and brain tau PET are robust quantitative biomarkers for studying ApoE ε4 by sex effects on brain tau deposition in MCI participants.
Keywords: tau deposition, ApoE ε4, mild cognitive impairment, 18F-AV-1451, partial volume correction
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact