13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(12):4042-4058. doi:10.7150/thno.84388 This issue Cite
Research Paper
HMGB1-mediated elevation of KLF7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through upregulating TLR4 and PTK2
1. State Key Laboratory of Holistic Integrative Management of Gastrointestinal Cancers and National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases, Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Institute of Liver and Gastrointestinal Diseases, Hubei Key Laboratory of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases, Tongji Hospital of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China.
3. Hubei Key Laboratory of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases; Hepatic Surgery Center, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology; Clinical Medicine Research Center for Hepatic Surgery of Hubei Province; Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Ministry of Education and Ministry of Public Health, Wuhan, Hubei, 430030, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
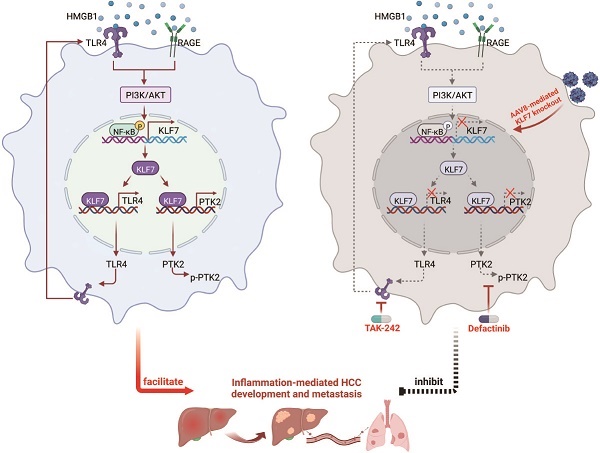
Background: Metastasis is a major cause of HCC-related deaths with no effective pharmacotherapies. Chronic inflammation promotes HCC dissemination, however, its underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of Krüppel-like factor 7 (KLF7) in inflammation-provoked HCC metastasis and proposed therapeutic strategies for KLF7-positive patients.
Methods: The expression of KLF7 in human HCC specimens were examined by immunohistochemistry and quantitative real-time PCR. The luciferase reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were conducted to explore the transcriptional regulation related to KLF7. Orthotopic xenograft models and DEN/CCl4-induced HCC models were established to evaluate HCC progression and metastasis.
Results: KLF7 overexpression promotes HCC metastasis through transactivating toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2) expression. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) upregulates KLF7 expression through the TLR4/advanced glycosylation end-product specific receptor (RAGE)-PI3K-AKT-NF-κB pathway, forming an HMGB1-KLF7-TLR4 positive feedback loop. The HMGB1-KLF7-TLR4/PTK2 axis is gradually activated during the progression of inflammation-HCC transition. Genetic depletion of KLF7 impedes HMGB1-mediated HCC progression and metastasis. The combined application of TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 and PTK2 inhibitor defactinib alleviates HCC progression and metastasis induced by the HMGB1-KLF7 axis. In human HCCs, KLF7 expression is positively correlated with cytoplasmic HMGB1, p-p65, TLR4, and PTK2 levels, and patients positively co-expressing HMGB1/KLF7, p-p65/KLF7, KLF7/TLR4 or KLF7/PTK2 exhibit the worst prognosis.
Conclusions: HMGB1-induced KLF7 overexpression facilitates HCC progression and metastasis by upregulating TLR4 and PTK2. Genetic ablation of KLF7 via AAV gene therapy and combined blockade of TLR4 and PTK2 represents promising therapy strategies for KLF7-positive HCC patients.
Keywords: krüppel-like factor 7, toll-like receptor 4, protein tyrosine kinase 2, high mobility group box 1, hepatocellular carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact