13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):176-202. doi:10.7150/thno.85409 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles as trackable efficient transporters of an experimental nanodrug with fibrotic heart and lung targeting
1. Instituto de Biomedicina y Biotecnología de Cantabria (IBBTEC), Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC)-Universidad de Cantabria (UC), Santander, Spain.
2. Center for Cooperative Research in Biomaterials (CIC biomaGUNE), Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), Paseo de Miramón 194, Donostia-San Sebastián 20014, Spain.
3. University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), 48940 Leioa, Spain.
4. Departamento de Anatomía y Biología Celular, Universidad de Cantabria, Santander, Spain.
5. Ikerbasque, Basque Foundation for Science, 48009 Bilbao, Spain.
6. Departamento de Fisiología y Farmacología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Cantabria, Santander, Spain.
Abstract
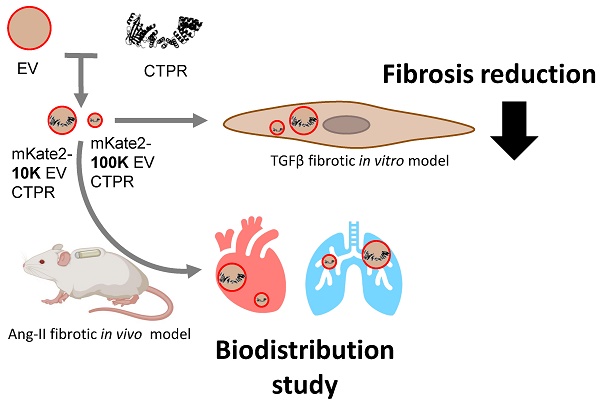
The discovery of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as efficient exogenous biotransporters of therapeutic agents into cells across biological membranes is an exciting emerging field. Especially the potential of EVs as targeted delivery systems for diseases with selective treatments, such as fibrosis, whose treatment causes side effects in other organs not involved in the disease. Methods: In this study, we collected embryonic fibroblast-derived EVs from two different centrifugation fractions, 10 K g and 100 K g fractions from a NIH-3T3 cell line loaded with an experimental drug. Mice with fibrotic hearts and lungs were obtained by administration of angiotensin II. We generated fluorescent EVs and bioluminescent drug to observe their accumulation by colocalization of their signals in fibrotic heart and lung. The biodistribution of the drug in various organs was obtained by detecting the Au present in the drug nanostructure. Results: The drug-loaded EVs successfully reduced fibrosis in pathological fibroblasts in vitro, and modified the biodistribution of the experimental drug, enabling it to reach the target organs in vivo. We described the pre-analytical characteristics of EVs related to physical variables, culture and harvesting conditions, crucial for their in vivo application as nanotransporters using a previously validated protein-based antifibrotic drug. The results showed the colocalization of EVs and the experimental drug in vivo and ex vivo and the efficient reduction of fibrosis in vitro. This work demonstrates that 10K-EVs and 100K-EVs derived from fibroblasts can act as effective biotransporters for targeted drug delivery to profibrotic fibroblasts, lungs, or heart.
Conclusion: We observed that fibroblast-derived 10K-EVs and 100K-EVs are useful biotransporters encapsulating a new generation drug leading to a reduction of fibrosis in profibrotic fibroblasts in vitro. In addition, drug containing EVs were shown to reach fibrotic heart and lungs in vivo, enhancing free drug biodistribution.
Keywords: biological antifibrotic nanocarriers, fibrosis, protein-nanomaterial hybrids, extracellular vesicles, in vivo imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact