13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2014; 4(9):931-944. doi:10.7150/thno.9663 This issue Cite
Review
Progress in Aptamer-Mediated Drug Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Targeting and Its Implications in Addressing Chemotherapeutic Challenges
1. Department of Neurology, Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400042, China.
2. Department of Anesthesia, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400037, China.
3. Department of Biomedical Materials Science, School of Biomedical Engineering, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400038, China
4. Department of Orthopedics, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400037, China.
5. Department of Orthopedics, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 02130, USA.
* These two authors contributed equally.
Abstract
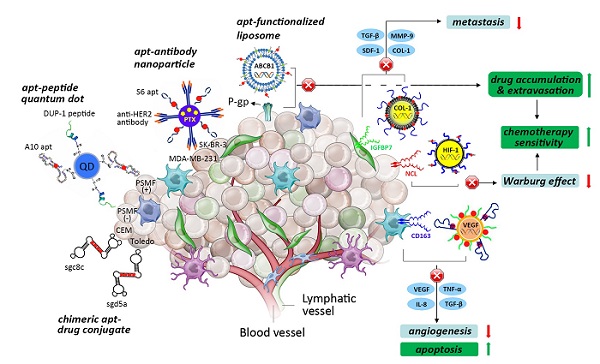
Aptamers are novel oligonucleotides with flexible three-dimensional configurations that recognize and bind to their cognate targets, including tumor surface receptors, in a high-affinity and highly specific manner. Because of their unique intrinsic properties, a variety of aptamer-mediated nanovehicles have been developed to directionally transport anti-cancer drugs to tumor sites to minimize systemic cytotoxicity and to enhance permeation by these tumoricidal agents. Despite advances in the selection and synthesis of aptamers and in the conjugation and self-assembly of nanotechnologies, current chemotherapy and drug delivery systems face great challenges. These challenges are due to the limitations of aptamers and vehicles and because of complicated tumor mechanisms, including heterogeneity, anti-cancer drug resistance, and hypoxia-induced aberrances. In this review, we will summarize current approaches utilizing tumor surface hallmarks and aptamers and their roles and mechanisms in therapeutic nanovehicles targeting tumors. Delivery forms include nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanogels, aptamer-drug conjugates, and novel molecular trains. Moreover, the obstacles posed by the aforementioned issues will be highlighted, and possible solutions will be acknowledged. Furthermore, future perspectives will be presented, including cutting-edge integration with RNA interference nanotechnology and personalized chemotherapy, which will facilitate innovative approaches to aptamer-based therapeutics.
Keywords: aptamer, biomarker, chemotherapy, drug delivery, nanomedicine.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact