13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(2):110-123. doi:10.7150/thno.9717 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Chitosan/siRNA Nanoparticles Targeting Cyclooxygenase Type 2 Attenuate Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction-induced Kidney Injury in Mice
1. Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Denmark;
2. Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Center, Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Aarhus University, Denmark.
*Chuanxu Yang and Line Nilsson contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
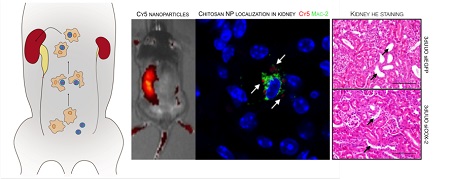
Cyclooxygenase type 2 (COX-2) plays a predominant role in the progression of kidney injury in obstructive nephropathy. The aim of this study was to test the efficacy of chitosan/small interfering RNA (siRNA) nanoparticles to knockdown COX-2 specifically in macrophages to prevent kidney injury induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Using optical imaging techniques and confocal microscopy, we demonstrated that chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles accumulated in macrophages in the obstructed kidney. Consistent with the imaging data, the obstructed kidney contained a higher amount of siRNA and macrophages. Chitosan-formulated siRNA against COX-2 was evaluated on RAW macrophages demonstrating reduced COX-2 expression and activity after LPS stimulation. Injection of COX-2 chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles in mice subjected to three-day UUO diminished the UUO-induced COX-2 expression. Likewise, macrophages in the obstructed kidney had reduced COX-2 immunoreactivity, and histological examination showed lesser tubular damage in COX-2 siRNA-treated UUO mice. Parenchymal inflammation, assessed by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 mRNA expression, was attenuated by COX-2 siRNA. Furthermore, treatment with COX-2 siRNA reduced heme oxygenase-1 and cleaved caspase-3 in UUO mice, indicating lesser oxidative stress and apoptosis. Our results demonstrate a novel strategy to prevent UUO-induced kidney damage by using chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles to knockdown COX-2 specifically in macrophages.
Keywords: Cyclooxygenase type 2, siRNA, chitosan, unilateral ureteral obstruction, mice.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact