13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(8):1176-1189. doi:10.7150/thno.12866 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Polymer-DNA Nanoparticle-Induced CXCR4 Overexpression Improves Stem Cell Engraftment and Tissue Regeneration in a Mouse Hindlimb Ischemia Model
1. Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
2. Medical Scientist Training Program, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
3. Department of Biology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
4. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
5. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
Abstract
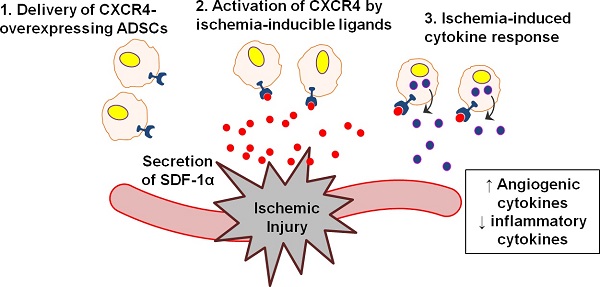
Peripheral arterial disease affects nearly 202 million individuals worldwide, sometimes leading to non-healing ulcers or limb amputations in severe cases. Genetically modified stem cells offer potential advantages for therapeutically inducing angiogenesis via augmented paracrine release mechanisms and tuned dynamic responses to environmental stimuli at disease sites. Here, we report the application of nanoparticle-induced CXCR4-overexpressing stem cells in a mouse hindlimb ischemia model. We found that CXCR4 overexpression improved stem cell survival, modulated inflammation in situ, and accelerated blood reperfusion. These effects, unexpectedly, led to complete limb salvage and skeletal muscle repair, markedly outperforming the efficacy of the conventional angiogenic factor control, VEGF. Importantly, assessment of CXCR4-overexpressing stem cells in vitro revealed that CXCR4 overexpression induced changes in paracrine signaling of stem cells, promoting a therapeutically desirable pro-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory phenotype. These results suggest that nanoparticle-induced CXCR4 overexpression may promote favorable phenotypic changes and therapeutic efficacy of stem cells in response to the ischemic environment.
Keywords: CXCR4
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact