13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(7):1966-1975. doi:10.7150/thno.16866 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Implantable and Biodegradable Macroporous Iron Oxide Frameworks for Efficient Regeneration and Repair of Infracted Heart
1. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P. R. China
2. Department of Anesthesiology, Division of Critical Care Medicine, Boston Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, 300 Longwood Avenue, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA
3. Department of Chemical Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria 3800, Australia
4. Department of Radiology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, P. R. China
5. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, P. R. China
6. National Supercomputer Research Center of Advanced Materials, Shandong Key Laboratory for High Strength Lightweight Metallic Materials, Advanced Materials Institute, Shandong Academy of Sciences, Jinan 250014, P. R. China
7. Department of Chemistry, Laboratory of Advanced Materials, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, P. R. China
* These authors contributed equally to this study
Abstract
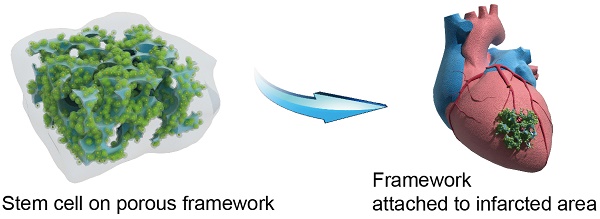
The construction, characterization and surgical application of a multilayered iron oxide-based macroporous composite framework were reported in this study. The framework consisted of a highly porous iron oxide core, a gelatin-based hydrogel intermediary layer and a matrigel outer cover, which conferred a multitude of desirable properties including excellent biocompatibility, improved mechanical strength and controlled biodegradability. The large pore sizes and high extent of pore interconnectivity of the framework stimulated robust neovascularization and resulted in substantially better cell viability and proliferation as a result of improved transport efficiency for oxygen and nutrients. In addition, rat models with myocardial infraction showed sustained heart tissue regeneration over the infract region and significant improvement of cardiac functions following the surgical implantation of the framework. These results demonstrated that the current framework might hold great potential for cardiac repair in patients with myocardial infraction.
Keywords: macroporous frameworks, vasculature, stem cell, blood iron pool, cardiac repair.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact