13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(10):2652-2672. doi:10.7150/thno.19680 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A Novel MPEG-PDLLA-PLL Copolymer for Docetaxel Delivery in Breast Cancer Therapy
State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, Collaborative Innovation Center of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan, China
Abstract
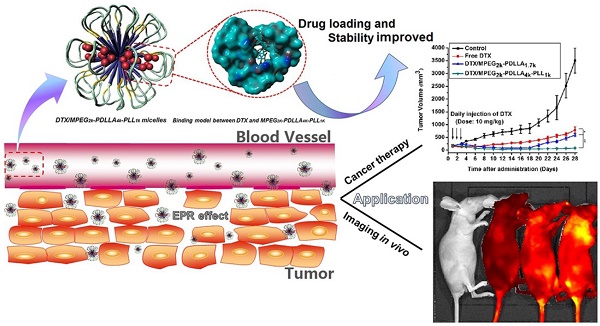
Satisfactory drug loading capacity and stability are the two main factors that determine the anti-cancer performance. In general, the stability of the micelles is reduced when the drug loading (DL) is increased. Therefore, it was a challenge to have high drug loading capacity and good stability. In this study, we introduced a hydrophilic poly (L-Lysine) (PLL) segment with different molecular-weights into the monomethoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (D, L-lactide) (MPEG-PDLLA) block copolymer to obtain a series of novel triblock MPEG-PDLLA-PLL copolymers. We found that the micelles formed by a specific MPEG2k-PDLLA4k-PLL1k copolymer could encapsulate docetaxel (DTX) with a satisfactory loading capacity of up to 20% (w/w) via the thin film hydration method, while the stability of drug loaded micellar formulation was still as good as that of micelles formed by MPEG2k-PDLLA1.7k with drug loading of 5% (w/w). The results from computer simulation study showed that compared with MPEG2k-PDLLA1.7k, the molecular chain of MPEG2k-PDLLA4k-PLL1k could form a more compact funnel-shaped structure when interacted with DTX. This structure favored keeping DTX encapsulated in the copolymer molecules, which improved the DL and stability of the nano-formulations. The in vitro and in vivo evaluation showed that the DTX loaded MPEG2k-PDLLA4k-PLL1k (DTX/MPEG2k-PDLLA4k-PLL1k) micelles exhibited more efficiency in tumor cell growth inhibition. In conclusion, the MPEG2k-PDLLA4k-PLL1k micelles were much more suitable than MPEG2k-PDLLA1.7k for DTX delivery, and then the novel nano-formulations showed better anti-tumor efficacy in breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: Docetaxel micelles, polymeric micelles, interaction, anti-tumor, drug loading capacity.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact