13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(10):2673-2689. doi:10.7150/thno.18915 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Microvesicles as Potential Biomarkers for the Identification of Senescence in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
1. Institute of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China;
2. Department of Bioinformatics and Systems Biology, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of the Ministry of Education, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China;
3. Department of Hematology, JingZhou Central Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Jingzhou, China;
4. Department of Hematology, Wuhan Central Hospital, Wuhan, China.
# These authors contributed equally to the study.
Abstract
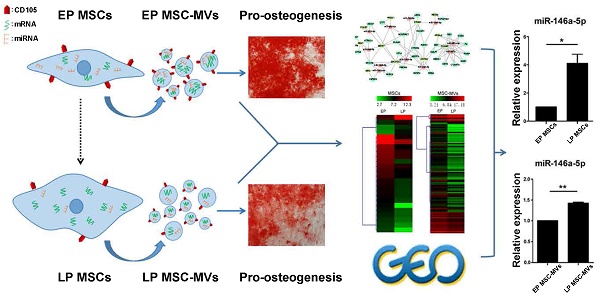
Senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) not only contributes to organism aging and the development of a variety of diseases but also severely impairs their therapeutic properties as a promising cell therapy. Studies searching for efficient biomarkers that represent cellular senescence have attracted much attention; however, no single marker currently provides an accurate cell-free representation of cellular senescence. Here, we studied characteristics of MSC-derived microvesicles (MSC-MVs) that may reflect the senescence in their parental MSCs. We found that senescent late passage (LP) MSCs secreted higher levels of MSC-MVs with smaller size than did early passage (EP) MSCs, and the level of CD105+ MSC-MVs decreased with senescence in the parental MSCs. Also, a substantially weaker ability to promote osteogenesis in MSCs was observed in LP than EP MSC-MVs. Comparative analysis of RNA sequencing showed the same trend of decreasing number of highly-expressed miRNAs with increasing number of passages in both MSCs and MSC-MVs. Most of the highly-expressed genes in LP MSCs and the corresponding MSC-MVs were involved in the regulation of senescence-related diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, based on the miRNA profiling, transcription factors (TF) and genes regulatory networks of MSC senescence, and the datasets from GEO database, we confirmed that expression of miR-146a-5p in MSC-MVs resembled the senescent state of their parental MSCs. Our findings provide evidence that MSC-MVs are a key factor in the senescence-associated secretory phenotype of MSCs and demonstrate that their integrated characteristics can dynamically reflect the senescence state of MSCs representing a potential biomarker for monitoring MSC senescence.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells, senescence, microvesicles, biomarker.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact