13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(14):3517-3526. doi:10.7150/thno.16359 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Real-time In vivo Diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using Rapid Fiber-Optic Raman Spectroscopy
1. Optical Bioimaging Laboratory, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117576;
2. Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore and National University Health System, Singapore 119260;
3. Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, National University of Singapore and National University Health System, Singapore 119074.
Abstract
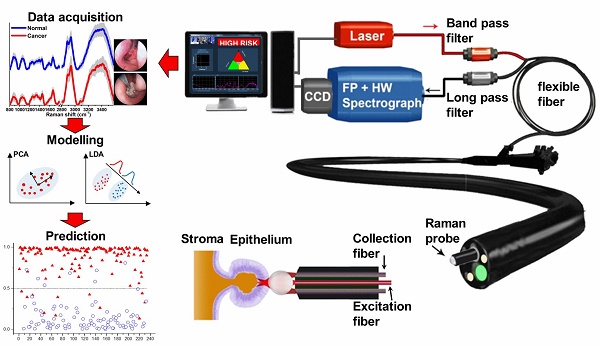
We report the utility of a simultaneous fingerprint (FP) (i.e., 800-1800 cm-1) and high-wavenumber (HW) (i.e., 2800-3600 cm-1) fiber-optic Raman spectroscopy developed for real-time in vivo diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) at endoscopy. A total of 3731 high-quality in vivo FP/HW Raman spectra (normal=1765; cancer=1966) were acquired in real-time from 204 tissue sites (normal=95; cancer=109) of 95 subjects (normal=57; cancer=38) undergoing endoscopic examination. FP/HW Raman spectra differ significantly between normal and cancerous nasopharyngeal tissues that could be attributed to changes of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and the bound water content in NPC. Principal components analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) together with leave-one subject-out, cross-validation (LOO-CV) were implemented to develop robust Raman diagnostic models. The simultaneous FP/HW Raman spectroscopy technique together with PCA-LDA and LOO-CV modeling provides a diagnostic accuracy of 93.1% (sensitivity of 93.6%; specificity of 92.6%) for nasopharyngeal cancer identification, which is superior to using either FP (accuracy of 89.2%; sensitivity of 89.9%; specificity of 88.4%) or HW (accuracy of 89.7%; sensitivity of 89.0%; specificity of 90.5%) Raman technique alone. Further receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis reconfirms the best performance of the simultaneous FP/HW Raman technique for in vivo diagnosis of NPC. This work demonstrates for the first time that simultaneous FP/HW fiber-optic Raman spectroscopy technique has great promise for enhancing real-time in vivo cancer diagnosis in the nasopharynx during endoscopic examination.
Keywords: Fiber-optic Raman spectroscopy, In vivo diagnosis, Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact