13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(5):1301-1311. doi:10.7150/thno.21979 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Non-invasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Chromosomal Aneuploidies and Microdeletion Syndrome Using Fetal Nucleated Red Blood Cells Isolated by Nanostructure Microchips
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynechology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071, China
2. Key Laboratory of Artificial Micro- and Nano-Structures of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430072, Hubei, China
3. Prenatal Diagnostic and Birth Health Clinical Research Center of Hubei Province, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071, China
4. Department of Prenatal Diagnostic Center, Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Hubei Province, Wuhan, Hubei, 430070, China
* equally contributing first author
# equally contributing senior authorship
Abstract
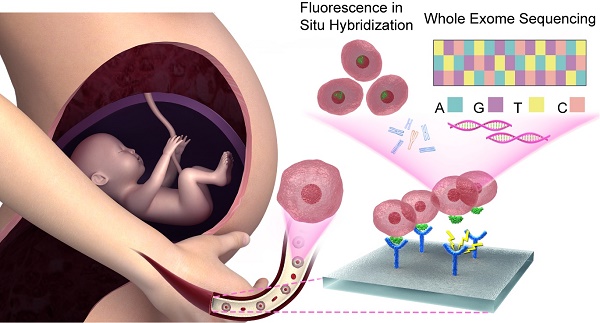
Detection of detached fetal nucleated red blood cells (fNRBCs) in the maternal peripheral blood may serve as a prospective testing method competing with the cell-free DNA, in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT).
Methods: Herein, we introduce a facile and effective lab-on-a-chip method of fNRBCs detection using a capture-releasing material that is composed of biotin-doped polypyrrole nanoparticles. To enhance local topographic interactions between the nano-components and fNRBC, a specific antibody, CD147, coated on the nanostructured substrate led to the isolation of fNRBCs from maternal peripheral blood. Subsequently, an electrical system was employed to release the captured cells using 0.8 V for 15 s. The diagnostic application of fNRBCs for fetal chromosomal disorders (Trisomy 13/21/18/X syndrome, microdeletion syndrome) was demonstrated.
Results: Cells captured by nanostructured microchips were identified as fNRBCs. Twelve cases of chromosomal aneuploidies and one case of 18q21 microdeletion syndrome were diagnosed using the fNRBCs released from the microchips.
Conclusion: Our method offers effective and accurate analysis of fNRBCs for comprehensive NIPT to monitor fetal cell development.
Keywords: non-invasive prenatal diagnosis, fetal nucleated red blood cells, nanostructure microchip, chromosomal aneuploidy, microdeletion syndrome
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact