13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(6):1740-1751. doi:10.7150/thno.22010 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Genomic analysis of liver cancer unveils novel driver genes and distinct prognostic features
1. Institute of Digestive Diseases and Department of Medicine & Therapeutics, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Diseases, LKS Institute of Health Sciences, CUHK Shenzhen Research Institute, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
2. Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
3. Department of Anatomical and Cellular Pathology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
4. Beijing Genomics Institute-Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518083, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
5. James D. Watson Institute of Genome Sciences, 310058, Hangzhou, People's Republic of China.
6. Public Laboratory, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy of Tianjin, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin 300060, People's Republic of China.
7. Department of Clinical Oncology, State Key Laboratory in Oncology in South China, Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
#XL and WX contributed equally to this work.
✉ Corresponding authors: Prof. Jun Yu, Institute of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, NT, Hong Kong. Tel: (852) 3763 6099; Fax: (852) 2144 5330; Email: junyu@cuhk.edu.hk; or Dr William KK Wu, Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, NT, Hong Kong. Tel: (852) 3505 3147; Fax: (852) 2637 2422; Email: wukakei@cuhk.edu.hk
Abstract
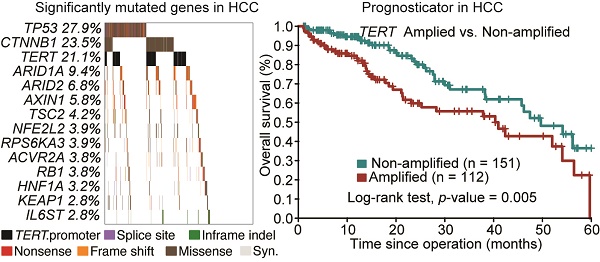
Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly heterogeneous disease with a dismal prognosis. However, driver genes and prognostic markers in HCC remain to be identified. It is hoped that in-depth analysis of HCC genomes in relation to available clinicopathological information will give rise to novel molecular prognostic markers.
Methods: We collected genomic data of 1,061 HCC patients from previous studies, and performed integrative analysis to identify significantly mutated genes and molecular prognosticators. We employed three MutSig algorithms (MutSigCV, MutSigCL and MutSigFN) to identify significantly mutated genes. The GISTIC2 algorithm was used to delineate focally amplified and deleted genomic regions. Nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) was utilized to decipher mutational signatures. Kaplan-Meier survival and Cox regression analyses were used to associate gene mutation and copy number alteration with survival outcome. Logistic regression model was applied to test association between gene mutation and mutational signatures.
Results: We discovered 11 novel driver genes, including RNF213, VAV3 and TNRC6B, with mutational prevalence ranging from 1% to 3%. Seven mutational signatures were also identified in HCC, some of which were associated with mutations of classical driver genes (e.g., TP53, TERT) as well as alcohol consumption. Focal amplifications of TERT and other druggable targets, including AURKA, were also revealed. Targeting AURKA by a small-molecule inhibitor potently induced apoptosis in HCC cells. We further demonstrated that HCC patients with TERT amplification displayed shortened overall survival independent of other clinicopathological parameters. In conclusion, our study identified novel cancer driver genes and prognostic markers in HCC, reiterating the translational importance of omics data in the precision medicine era.
Keywords: HCC, mutation, TERT, prognostic marker, druggable target
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact