13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(14):3841-3855. doi:10.7150/thno.25784 This issue Cite
Research Paper
HSP40 co-chaperone protein Tid1 suppresses metastasis of head and neck cancer by inhibiting Galectin-7-TCF3-MMP9 axis signaling
1. Institute of Oral Biology, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
2. Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
3. Department of Dentistry, School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
4. Department of Stomatology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
5. Department of Medical Research and Education, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
6. Graduate Institute of Chinese Medical Science and Institute of Medical Science, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
7. Institute of Basic Medical Science, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
8. Department of Health and Nutrition Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan
9. Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan
10. Genome Research Center, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
11. Department of Dentistry, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
12. Cancer Progression Center of Excellence, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
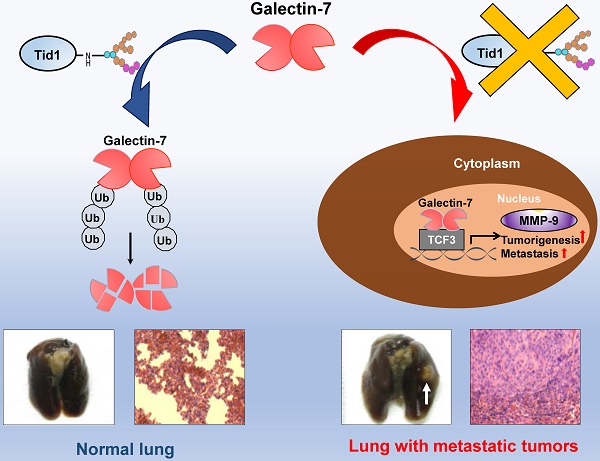
Human tumorous imaginal disc (Tid1), a DnaJ co-chaperone protein, is classified as a tumor suppressor. Previously, we demonstrated that Tid1 reduces head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) malignancy. However, the molecular details of Tid1-mediated anti-metastasis remain elusive.
Methods: We used affinity chromatography and systemic mass spectrometry to identify Tid1-interacting client proteins. Immunohistochemical staining of Tid1 in HNSCC patient tissues was examined to evaluate the association between the expression profile of Tid1-interacting client proteins with pathologic features and prognosis. The roles of Tid1-interacting client proteins in metastasis were validated both in vitro and in vivo. The interacting partner and downstream target of Tid1-interacting client protein were determined.
Results: Herein, we first revealed that Galectin-7 was one of the Tid1-interacting client proteins. An inverse association of protein expression profile between Tid1 and Galectin-7 was determined in HNSCC patients. Low Tid1 and high Galectin-7 expression predicted poor overall survival in HNSCC. Furthermore, Tid1 abolished the nuclear translocation of Galectin-7 and suppressed Galectin-7-induced tumorigenesis and metastasis. Keratinocyte-specific Tid1-deficient mice with 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO) treatment exhibited increased protein levels of Galectin-7 and had a poor survival rate. Tid1 interacted with Galectin-7 through its N-linked glycosylation to promote Tid1-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Galectin-7. Additionally, Galectin-7 played a critical role in promoting tumorigenesis and metastatic progression by enhancing the transcriptional activity of TCF3 transcription factor through elevating MMP-9 expression.
Conclusions: Overall, future treatments through activating Tid1 expression or inversely repressing the oncogenic function of Galectin-7 may exhibit great potential in targeting HNSCC progression.
Keywords: HSP40, tumor metastasis, MMP-9, Tid1, Galectin-7, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact