13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(21):5986-5994. doi:10.7150/thno.26650 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Chemoresistance Transmission via Exosome-Mediated EphA2 Transfer in Pancreatic Cancer
1. School of Biological and Health Systems Engineering, Virginia G. Piper Biodesign Center for Personalized Diagnostics, The Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85281, USA.
2. Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin 300060, PR China.
3. Division of Radiation Oncology, University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
4. Research Center of Basic Medical Sciences & Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, PR China.
5. Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics, The Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85281, USA.
6. Department of Nanomedicine, Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
7. Molecular Medicine Division, Translational Genomics Research Institute, Phoenix, AZ 85004, USA.
8. Department of Surgical Oncology, Division of Surgery, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
9. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Center, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
10. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY 10065, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
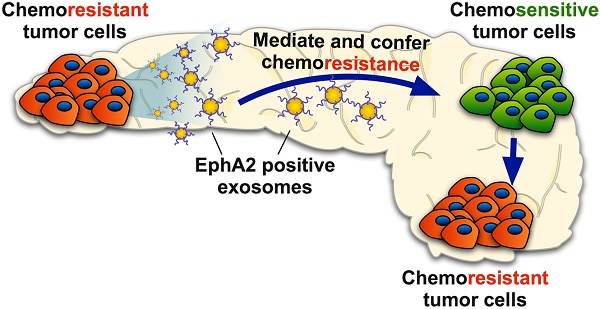
Rationale: Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles secreted by most cells that are found in blood and other bodily fluids, and which contain cytoplasmic material and membrane factors corresponding to their cell type of origin. Exosome membrane factors and contents have been reported to alter adjacent and distant cell behavior in multiple studies, but the impact of cancer-derived exosomes on chemoresistance is less clear.
Methods: Exosomes isolated from three pancreatic cancer (PC) cell lines displaying variable gemcitabine (GEM) resistance (PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and BxPC-3) were tested for their capacity to transmit chemoresistance among these cell lines. Comparative proteomics was performed to identify key exosomal proteins that conferred chemoresistance. Cell survival was assessed in GEM responsive PC cell lines treated with recombinant Ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EphA2), a candidate chemoresistance transfer factor, or exosomes from a chemoresistant PC cell line treated with or without EphA2 shRNA.
Results: Exosomes from chemoresistant PANC-1 cells increased the GEM resistance of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cell cultures. Comparative proteomics determined that PANC-1 exosomes overexpressed Ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EphA2) versus exosomes of less chemoresistant PC cell lines MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3. EphA2-knockdown in PANC-1 cells inhibited their ability to transmit exosome-mediated chemoresistance to MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3, while treatment of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells with soluble EphA2 did not promote chemoresistance, indicating that membrane carried EphA2 was important for the EphA2 chemoresistance effect.
Conclusion: Exosomal EphA2 expression could transmit chemoresistance and may potentially serve as a minimally-invasive predictive biomarker for PC treatment response. Further work should address whether additional exosomal factors regulate resistance to other cancer therapeutic agents for PC or other cancer types.
Keywords: Exosome, EphA2, Cytotoxic resistance, Pancreatic cancer, Gemcitabine
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact