13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(9):4351-4362. doi:10.7150/thno.52436 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ultrasound-mediated augmented exosome release from astrocytes alleviates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity
Paul C.Lauterbur research center for biomedical imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, People's Republic of China. 1068 Xueyuan Avenue, Shenzhen University Town, Shenzhen, 518055, China.
Abstract
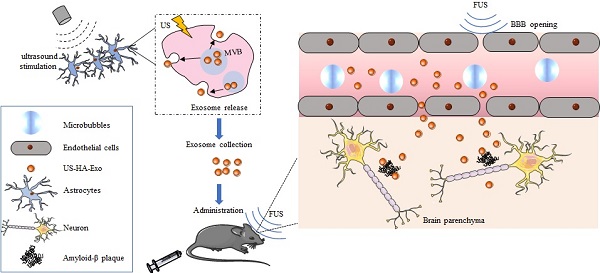
Background: Extracellular vesicles, including exosomes, are secreted by a variety of cell types in the central nervous system. Exosomes play a role in removing intracellular materials from the endosomal system. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is caused by an overproduction or reduced amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide clearance. Increased Aβ levels in the brain may impair the exosome-mediated Aβ clearance pathway. Therapeutic ultrasound stimulation demonstrated its potential for promoting Aβ degradation efficiency in clinical trials. However, the underlying mechanism of ultrasound stimulation is still unclear.
Methods: In this study, astrocytes, the most abundant glial cells in the brain, were used for exosome production. Post insonation, exosomes from ultrasound-stimulated HA cells (US-HA-Exo) were collected, nanoparticle tracking analysis and protein analysis were used to measure and characterize exosomes. Neuroprotective effect of US-HA-Exo in oligomeric Aβ42 toxicated SH-SY5Y cells was tested. Cellular uptake and distribution of exosomes were observed by flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Focused ultrasound (FUS) with microbubbles was employed for blood-brain-barrier opening to achieve brain-targeted exosome delivery. After US-HA-Exo/FUS treatment, amyloid-β plaque in APP/PS1 mice were evaluated by Aβ immunostaining and thioflavin-S staining.
Results: We showed that ultrasound resulted in an almost 5-fold increase in the exosome release from human astrocytes. Exosomes were rapidly internalized in SH-SY5Y cells, and colocalized with FITC-Aβ42, causing a decreased uptake of FITC-Aβ42. CCk-8 test results showed that US-HA-Exo could mitigate Aβ toxicity to neurons in vitro. The therapeutic potential of US-HA-Exo/FUS delivery was demonstrated by a decrease in thioflavin-S-positive amyloid plaques and Aβ immuno-staining, a therapeutic target for AD in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. The iTRAQ-based proteomic quantification was performed to gain mechanistic insight into the ultrasound effect on astrocyte-derived exosomes and their ability to alleviate Aβ neurotoxicity.
Conclusion: Our results imply that US-HA-Exo have the potential to provide neuroprotective effects to reverse oligomeric amyloid-β-induced cytotoxicity in vitro and, when combined with FUS-induced BBB opening, enable the clearance of amyloid-β plaques in vivo.
Keywords: ultrasound stimulation, astrocytes, exosomes, Alzheimer's disease, iTRAQ
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact