13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(9):4549-4566. doi:10.7150/thno.54967 This issue Cite
Review
The crosstalk between m6A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: a novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling
1. Department of Pathology, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310000, China.
2. Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310000, China.
Abstract
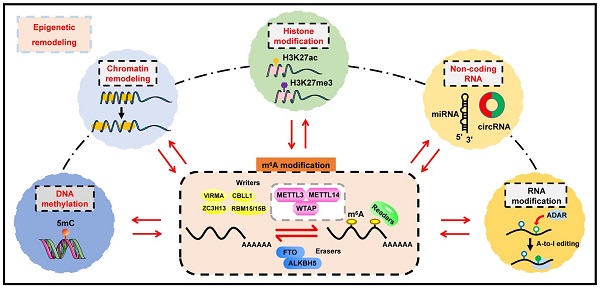
Epigenetic regulation involves a range of sophisticated processes which contribute to heritable alterations in gene expression without altering DNA sequence. Regulatory events predominantly include DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, histone modifications, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), and RNA modification. As the most prevalent RNA modification in eukaryotic cells, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation actively participates in the modulation of RNA metabolism. Notably, accumulating evidence has revealed complicated interrelations occurring between m6A and other well-known epigenetic modifications. Their crosstalk conspicuously triggers epigenetic remodeling, further yielding profound impacts on a variety of physiological and pathological processes, especially tumorigenesis. Herein, we provide an up-to-date review of this emerging hot area of biological research, summarizing the interplay between m6A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators, and highlighting their underlying functions in epigenetic reprogramming.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine (m6A), DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, histone modification, non-coding RNA (ncRNA), RNA modification
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact