13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):7671-7684. doi:10.7150/thno.61881 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Snail1 expression in endothelial cells controls growth, angiogenesis and differentiation of breast tumors
1. Programa de Recerca en Càncer, Institut Hospital del Mar d'Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM), Unidad Asociada al CSIC, Barcelona, Spain.
2. Departament de Ciències Experimentals i de la Salut, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain.
3. Servei d'Anatomia Patològica, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Spain.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
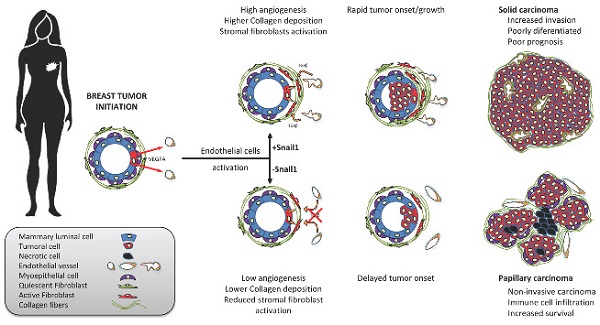
Snail1 is a transcriptional factor required for epithelial to mesenchymal transition and activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF). Apart from that, tumor endothelial cells also express Snail1. Here, we have unraveled the role of Snail1 in this tissue in a tumorigenic context.
Methods: We generated transgenic mice with an endothelial-specific and inducible Snail1 depletion. This murine line was crossed with MMTV-PyMT mice that develop mammary gland tumors and the consequence of Snail1 depletion in the endothelium were investigated. We also interfere Snail1 expression in cultured endothelial cells.
Results: Specific Snail1 depletion in the endothelium of adult mice does not promote an overt phenotype; however, it delays the formation of mammary gland tumors in MMTV-PyMT mice. These effects are associated to the inability of Snail1-deficient endothelial cells to undergo angiogenesis and to enhance CAF activation in a paracrine manner. Moreover, tumors generated in mice with endothelium-specific Snail1 depletion are less advanced and show a papillary phenotype. Similar changes on onset and tumor morphology are observed by pretreatment of MMTV-PyMT mice with the angiogenic inhibitor Bevacizumab. Human breast papillary carcinomas exhibit a lower angiogenesis and present lower staining of Snail1, both in endothelial and stromal cells, compared with other breast neoplasms. Furthermore, human breast tumors datasets show a strong correlation between Snail1 expression and high angiogenesis.
Conclusion: These findings show a novel role for Snail1 in endothelial cell activation and demonstrate that these cells impact not only on angiogenesis, but also on tumor onset and phenotype.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact