13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):7779-7796. doi:10.7150/thno.58729 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting KDM4B that coactivates c-Myc-regulated metabolism to suppress tumor growth in castration-resistant prostate cancer
1. Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Department of Life Science, National Tsing-Hua University, Hsinchu 30013, Taiwan.
2. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung 40705, Taiwan.
3. School of Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, 40201, Taiwan.
4. Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan 333, Taiwan.
5. Institute of Cellular and System Medicine, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli 35053, Taiwan.
6. Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica, Taipei, 11529, Taiwan.
7. Division of Breast Surgery, General Surgery, Department of Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Linko Medical Center, Taoyuan 333, Taiwan.
8. Graduate Institute of Cancer Biology and Drug Discovery, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 110, Taiwan.
9. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of California Davis School of Medicine, University of California Davis Cancer Centre, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA.
Abstract
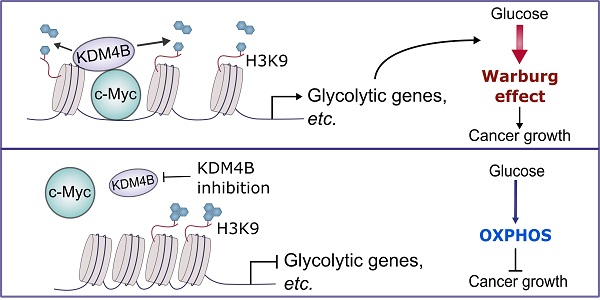
Rationale: The progression of prostate cancer (PCa) to castration-resistant PCa (CRPC) despite continuous androgen deprivation therapy is a major clinical challenge. Over 90% of patients with CRPC exhibit sustained androgen receptor (AR) signaling. KDM4B that removes the repressive mark H3K9me3/2 is a transcriptional activator of AR and has been implicated in the development of CRPC. However, the mechanisms of KDM4B involvement in CRPC remain largely unknown. Here, we sought to demonstrate the molecular pathway mediated by KDM4B in CRPC and to provide proof-of-concept evidence that KDM4B is a potential CRPC target.
Methods: CRPC cells (C4-2B or CWR22Rv1) depleted with KDM4B followed by cell proliferation (in vitro and xenograft), microarray, qRT-PCR, Seahorse Flux, and metabolomic analyses were employed to identify the expression and metabolic profiles mediated by KDM4B. Immunoprecipitation was used to determine the KDM4B-c-Myc interaction region. Reporter activity assay and ChIP analysis were used to characterize the KDM4B-c-Myc complex-mediated mechanistic actions. The clinical relevance between KDM4B and c-Myc was determined using UCSC Xena analysis and immunohistochemistry.
Results: We showed that KDM4B knockdown impaired CRPC proliferation, switched Warburg to OXPHOS metabolism, and suppressed gene expressions including those targeted by c-Myc. We further demonstrated that KDM4B physically interacted with c-Myc and they were co-recruited to the c-Myc-binding sequence on the promoters of metabolic genes (LDHA, ENO1, and PFK). Importantly, KDM4B and c-Myc synergistically promoted the transactivation of the LDHA promoter in a demethylase-dependent manner. We also provided evidence that KDM4B and c-Myc are co-expressed in PCa tissue and that high expression of both is associated with worse clinical outcome.
Conclusions: KDM4B partners with c-Myc and serves as a coactivator of c-Myc to directly enhance c-Myc-mediated metabolism, hence promoting CRPC progression. Targeting KDM4B is thus an alternative therapeutic strategy for advanced prostate cancers driven by c-Myc and AR.
Keywords: Castration-resistant prostate cancer, KDM4B, c-Myc, histone demethylase, metabolic rewiring
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact