13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):7970-7983. doi:10.7150/thno.62138 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Environmentally-induced mdig contributes to the severity of COVID-19 through fostering expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor NRPs and glycan metabolism
1. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Wayne State University, 259 Mack Avenue, Detroit, MI 48201, USA.
2. Stony Brook Cancer Center and Department of Pathology, Stony Brook University, Lauterbur Drive, Stony Brook, NY 11794, USA.
3. Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, School of Medicine, Wayne State University, 540 E. Canfield St, Detroit, MI 48201, USA.
Abstract
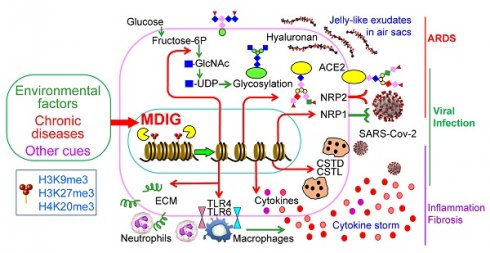
The novel β-coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has infected more than 177 million people and resulted in 3.84 million death worldwide. Recent epidemiological studies suggested that some environmental factors, such as air pollution, might be the important contributors to the mortality of COVID-19. However, how environmental exposure enhances the severity of COVID-19 remains to be fully understood. In the present report, we provided evidence showing that mdig, a previously reported environmentally-induced oncogene that antagonizes repressive trimethylation of histone proteins, is an important regulator for SARS-CoV-2 receptors neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and NRP2, cathepsins, glycan metabolism and inflammation, key determinants for viral infection and cytokine storm of the patients. Depletion of mdig in bronchial epithelial cells by CRISPR-Cas-9 gene editing resulted in a decreased expression of NRP1, NRP2, cathepsins, and genes involved in protein glycosylation and inflammation, largely due to a substantial enrichment of lysine 9 and/or lysine 27 trimethylation of histone H3 (H3K9me3/H3K27me3) on these genes as determined by ChIP-seq. Meanwhile, we also validated that environmental factor arsenic is able to induce mdig, NRP1 and NRP2, and genetic disruption of mdig lowered expression of NRP1 and NRP2. Furthermore, mdig may coordinate with the Neanderthal variants linked to an elevated mortality of COVID-19. These data, thus, suggest that mdig is a key mediator for the severity of COVID-19 in response to environmental exposure and targeting mdig may be the one of the effective strategies in ameliorating the symptom and reducing the mortality of COVID-19.
Keywords: mdig, COVID-19, NRP1, NRP2, Glycosylation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact