13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):8092-8111. doi:10.7150/thno.58739 This issue Cite
Research Paper
N-terminus-independent activation of c-Src via binding to a tetraspan(in) TM4SF5 in hepatocellular carcinoma is abolished by the TM4SF5 C-terminal peptide application
1. Department of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea
2. Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea
3. Global AI Drug Discovery Center, College of Pharmacy and Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 03760, Republic of Korea
4. College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, Seoul 06974, Republic of Korea
5. Interdisciplinary Program in Genetic Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
*Equally contributed
Abstract
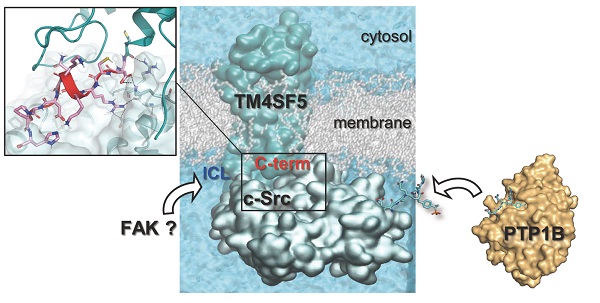
Active c-Src non-receptor tyrosine kinase localizes to the plasma membrane via N-terminal lipid modification. Membranous c-Src causes cancer initiation and progression. Even though transmembrane 4 L six family member 5 (TM4SF5), a tetraspan(in), can be involved in this mechanism, the molecular and structural influence of TM4SF5 on c-Src remains unknown.
Methods: Here, we investigated molecular and structural details by which TM4SF5 regulated c-Src devoid of its N-terminus and how cell-penetrating peptides were able to interrupt c-Src activation via interference of c-Src-TM4SF5 interaction in hepatocellular carcinoma models.
Results: The TM4SF5 C-terminus efficiently bound the c-Src SH1 kinase domain, efficiently to the inactively-closed form. The complex involved protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B able to dephosphorylate Tyr530. The c-Src SH1 domain alone, even in a closed form, bound TM4SF5 to cause c-Src Tyr419 and FAK Y861 phosphorylation. Homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulation studies predicted the directly interfacing residues, which were further validated by mutational studies. Cell penetration of TM4SF5 C-terminal peptides blocked the interaction of TM4SF5 with c-Src and prevented c-Src-dependent tumor initiation and progression in vivo.
Conclusions: Collectively, these data demonstrate that binding of the TM4SF5 C-terminus to the kinase domain of inactive c-Src leads to its activation. Because this binding can be abolished by cell-penetrating peptides containing the TM4SF5 C-terminus, targeting this direct interaction may be an effective strategy for developing therapeutics that block the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: c-Src, metastasis, protein-protein interaction, PTPIB, TM4SF5
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact