13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(19):9311-9330. doi:10.7150/thno.60265 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Therapeutic potential of garlic chive-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory diseases
1. Department of Nutrition and Health Sciences, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, 230 Filley Hall, Lincoln, NE 68583-0922, USA.
2. Center for Biotechnology, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, E117 Beadle Center, Lincoln, NE 68588-0665, USA.
3. Proteomics and Metabolomics Facility, Nebraska Center for Biotechnology, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, N300 Beadle Center, NE 68588-0115, USA.
4. Department of Statistics, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, 354B Hardin Hall, Lincoln, NE 68583-0963, USA.
5. Department of Biochemistry, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, N217 Beadle Center, Lincoln, NE 68588-0665, USA.
6. Department of Biochemistry, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, N158 Beadle Center, Lincoln, NE 68588-0665, USA.
7. Department of Nutrition, University of Massachusetts Amherst, 211 Chenoweth Laboratory, 100 Holdsworth Way, Amherst, MA 01003, USA.
8. School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Rd, Shanghai, 200240, China.
Abstract
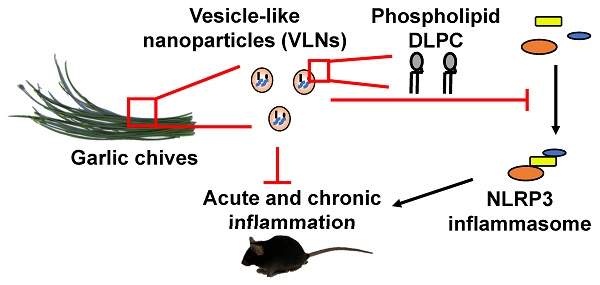
Aberrant activation of the nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat related (NLR) family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome drives the development of many complex inflammatory diseases, such as obesity, Alzheimer's disease, and atherosclerosis. However, no medications specifically targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome have become clinically available. Therefore, we aim to identify new inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome in this study.
Methods: Vesicle-like nanoparticles (VLNs) were extracted from garlic chives and other Allium vegetables and their effects on the NLRP3 inflammasome were evaluated in primary macrophages. After garlic chive-derived VLNs (GC-VLNs) were found to exhibit potent anti-NLRP3 inflammasome activity in cell culture, such function was further assessed in a murine acute liver injury disease model, as well as in diet-induced obesity. Finally, GC-VLNs were subjected to omics analysis to identify the active components with anti-NLRP3 inflammasome function.
Results: GC-VLNs are membrane-enclosed nanoparticles containing lipids, proteins, and RNAs. They dose-dependently inhibit pathways downstream of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, including caspase-1 autocleavage, cytokine release, and pyroptotic cell death in primary macrophages. The inhibitory effects of GC-VLNs on the NLRP3 inflammasome are specific, considering their marginal impact on activation of other inflammasomes. Local administration of GC-VLNs in mice alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in chemical-induced acute liver injury. When administered orally or intravenously, GC-VLNs accumulate in specific tissues and suppress activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and chronic inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. The phospholipid 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DLPC) in GC-VLNs has been identified to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Conclusions: Identification of GC-VLNs and their active component DLPC as potent inflammasome inhibitors provides new therapeutic candidates in the treatment of NLRP3 inflammasome-driven diseases.
Keywords: Nanoparticles, vesicles, garlic chive, NLRP3 inflammasome, obesity
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact