13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(19):9705-9720. doi:10.7150/thno.61731 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Proteomic analysis of lung cancer cells reveals a critical role of BCAT1 in cancer cell metastasis
1. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Taizhou People's Hospital, Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Taizhou, Jiangsu 225300, China.
3. Durbrain Medical Laboratory, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310000, China.
Abstract
Metastasis is the major cause of high mortality in lung cancer. Exploring the underlying mechanisms of metastasis thus holds promise for identifying new therapeutic strategies that may enhance survival.
Methods: We applied quantitative mass spectrometry to compare protein expression profiles between primary and metastatic lung cancer cells whilst investigating metastasis-related molecular features.
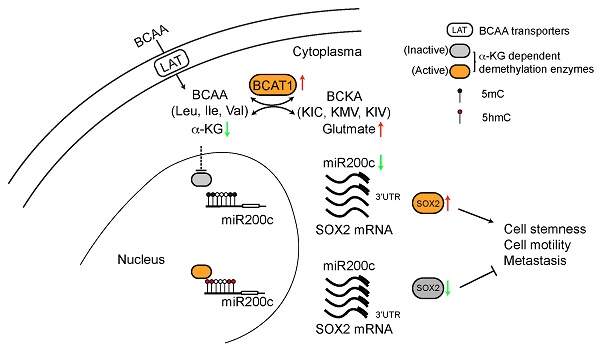
Results: We discovered that BCAT1, the key enzyme in branched-chain amino acid metabolism, is overexpressed at the protein level in metastatic lung cancer cells, as well as in metastatic tissues from lung cancer patients. Analysis of transcriptomic data available in the TCGA database revealed that increased BCAT1 transcription is associated with poor overall survival of lung cancer patients. In accord with a critical role in metastasis, shRNA-mediated knockdown of BCAT1 expression reduced migration of metastatic cells in vitro and the metastasis of these cells to distal organs in nude mice. Mechanistically, high levels of BCAT1 depleted α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and promoted expression of SOX2, a transcription factor regulating cancer cell stemness and metastasis.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that BCAT1 plays an important role in promoting lung cancer cell metastasis, and may define a novel pathway to target as an anti-metastatic therapy.
Keywords: BCAT1, SOX2, stemness, metastasis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact