13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(3):1303-1320. doi:10.7150/thno.67702 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hedgehog signaling is controlled by Rac1 activity
1. National Clinical Research Center for Child Health of the Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, 310052, China
2. Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310058, China
Abstract
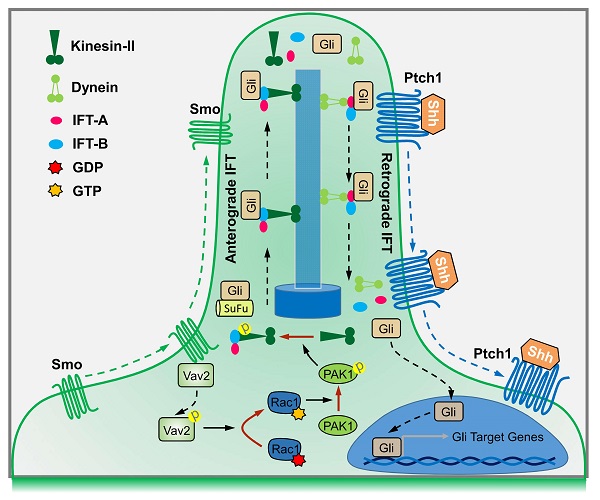
Rationale: The nuclear translocation of transcriptional factor Gli is indispensable for Hedgehog (Hh) signaling activation, whose deregulation causes cancer progressions; however, the mechanisms governing Gli nuclear translocation are poorly understood. Here, we report that the Gli translocation in response to Hh requires Rac1 activation.
Methods: C3H10T1/2 cell line and mouse embryonic fibroblasts were used to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying Rac1 activity in regulation of Hh signaling transduction. Transgenic mouse strains and human medulloblastoma (MB) tissue samples were utilized to examine the role of Rac1 in Hh-directed limb bud development and MB progression.
Results: We show that upon the binding of Hh to receptor Patched1 (Ptch1), receptor Smoothened (Smo) dissociates from Ptch1 and binds to Vav2, resulting in the increased phosphorylation levels of Vav2 at Y172, which further activates Rac1. The role of Rac1 is dependent on the regulation of phosphorylation levels of KIF3A at S689 and T694, which in turn affects IFT88 stability and subsequently dampens SuFu-Gli complex formation, leading to the release of Gli from the complex and the consequent translocation of Gli into the nucleus. Moreover, Vav2 phospho-Y172 levels are up-regulated in GFAP-Cre;SmoM2+/- mouse cerebellum and human Shh type MB tissues, whereas deficiency of Rac1 in mouse embryonic limb bud ectoderm (Prx1-Cre;Rac1f/f) impedes Hh activation by disruption of Gli nuclear translocation.
Conclusion: Together, our results uncover the Rac1 activation and the subsequent Gli translocation as a hitherto uncharacterized mechanism controlling Hh signaling and may provide targets for therapeutic intervention of this signaling pathway.
Keywords: Rac1, Vav2, PAK1, IFT, KIF, Hedgehog, Gli
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact